Thermal Insulation Materials Testing: A Guide
If you are involved in the construction or manufacturing industry, you know how important thermal insulation materials are. They help maintain a stable temperature in buildings and equipment, reducing energy consumption and costs. However, to ensure that these materials work effectively, you need to test them for their thermal conductivity and other properties. This is where thermal insulation materials testing comes in.
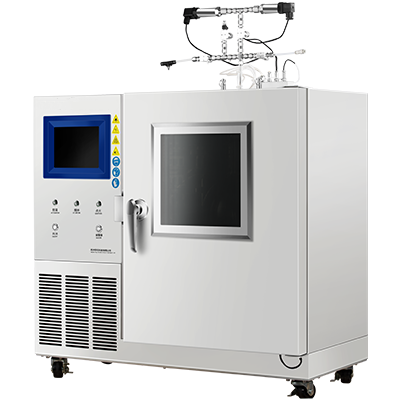
Thermal insulation materials testing is a process of evaluating the performance of insulation materials under different conditions. It involves measuring the thermal conductivity, density, thickness, and other characteristics of the material to ensure that it meets the required standards. The tests are conducted using specialized equipment and techniques to ensure accuracy and reliability. By testing your insulation materials, you can ensure that they are safe, efficient, and effective in their intended application.
Whether you are a manufacturer of insulation materials or a contractor using these materials in your projects, thermal insulation materials testing is essential to ensure that your products or projects are of high quality and meet the required standards. With the right testing procedures and equipment, you can have the confidence that your insulation materials will perform as intended, reducing energy consumption and costs while maintaining a comfortable environment.
Fundamentals of Thermal Insulation
Thermal insulation is a crucial aspect of energy conservation in buildings and industrial processes. It refers to the materials used to reduce the rate of heat transfer from one surface to another. Thermal insulation materials can be classified into three categories: organic, inorganic, and composite materials. These materials are used in various applications, including building insulation, refrigeration, and cryogenics.
Thermal Properties Measurement
Thermal insulation materials are characterized by their thermal properties, including thermal conductivity, thermal resistance, and thermal diffusivity. Thermal conductivity refers to the rate at which heat is transferred through a material. It is measured in W/mK and is dependent on the temperature, density, and moisture content of the material.
Thermal resistance is the reciprocal of thermal conductivity and is measured in m2K/W. It represents the ability of a material to resist heat flow. The higher the thermal resistance, the better the insulation performance of the material.
Thermal diffusivity is a measure of the rate at which heat is conducted through a material. It is measured in m2/s and is dependent on the thermal conductivity, density, and specific heat capacity of the material.
Material Classification
Thermal insulation materials can be classified into three categories: organic, inorganic, and composite materials. Organic materials, such as cellulose, wool, and foam, are derived from natural sources. Inorganic materials, such as glass, ceramic, and mineral wool, are derived from non-living sources. Composite materials, such as aerogel and vacuum insulation panels, are made up of a combination of organic and inorganic materials.
Each type of thermal insulation material has its own unique properties and characteristics. For example, organic materials are generally more environmentally friendly and have better acoustic insulation properties, while inorganic materials are more resistant to fire and have higher thermal stability. Composite materials, on the other hand, offer a combination of the benefits of both organic and inorganic materials.
In conclusion, understanding the fundamentals of thermal insulation is crucial in selecting the right material for a specific application. By considering the thermal properties and material classification, you can choose the most appropriate thermal insulation material for your needs.
Standard Test Methods
When it comes to thermal insulation materials testing, there are several standard test methods that are commonly used. These methods are designed to ensure that the materials being tested meet certain quality and performance standards. In this section, we will discuss two of the most common types of standards: ASTM and ISO.
ASTM Standards
The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) has developed a number of standards for testing thermal insulation materials. These standards cover a wide range of topics, including the measurement of thermal conductivity, the determination of compressive strength, and the evaluation of fire resistance.
One of the most commonly used ASTM standards for thermal insulation materials testing is C518, which is used to measure the thermal conductivity of materials. This test involves placing a sample of the material between two plates, applying a temperature difference across the plates, and measuring the rate of heat transfer through the material.
Another important ASTM standard is C177, which is used to measure the thermal conductivity of materials at high temperatures. This test involves heating a sample of the material to a specific temperature and then measuring the rate of heat transfer through the material.
ISO Standards
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has also developed a number of standards for testing thermal insulation materials. These standards cover many of the same topics as the ASTM standards, but they are designed to be used by companies and organizations around the world.
One of the most commonly used ISO standards for thermal insulation materials testing is ISO 8301, which is used to measure the thermal conductivity of materials. This test is similar to the ASTM C518 test, but it includes additional requirements for the size and shape of the test samples.
Another important ISO standard is ISO 8990, which is used to determine the thermal insulation properties of buildings. This standard includes requirements for the measurement of thermal resistance, thermal transmittance, and thermal bridging in buildings.
Overall, these standards play an important role in ensuring that thermal insulation materials meet certain quality and performance standards. By following these standards, companies and organizations can ensure that their products are safe, effective, and reliable.
Performance Testing
When it comes to thermal insulation materials testing, performance testing is an essential step in ensuring that the materials meet the required standards. Thermal insulation materials are designed to reduce heat transfer from one area to another, and performance testing helps to determine how well they do this.
Thermal Resistance
Thermal resistance is a key factor in determining the effectiveness of insulation materials. It is a measure of how well a material resists heat flow, and is expressed in units of R-value. The higher the R-value, the better the insulation.
Thermal resistance testing involves measuring the R-value of the insulation material. This is done by placing the material between two plates, and measuring the temperature difference between the plates. The R-value is then calculated based on the temperature difference and the thickness of the material.
Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity is another important factor in determining the effectiveness of insulation materials. It is a measure of how well a material conducts heat, and is expressed in units of W/mK. The lower the thermal conductivity, the better the insulation.
Thermal conductivity testing involves measuring the heat flow through the insulation material. This is done by applying a temperature difference across the material, and measuring the resulting heat flow. The thermal conductivity is then calculated based on the temperature difference and the thickness of the material.
Fire Performance
Fire performance is also an important consideration when it comes to insulation materials. Insulation materials can be a fire hazard if they are not properly designed and tested.
Fire performance testing involves exposing the insulation material to a flame, and measuring its reaction. The material is typically tested for flame spread, smoke development, and heat release. If the material meets the required standards for fire performance, it can be considered safe to use in buildings and other applications.
In summary, performance testing is an essential step in ensuring that thermal insulation materials meet the required standards for thermal resistance, thermal conductivity, and fire performance. By testing these factors, you can be confident that the insulation materials will provide effective insulation and be safe to use in a variety of applications.
Durability Assessments
When selecting a thermal insulation material, it is important to consider its durability. Durability assessments can help determine how well a material will perform over time in different environments. Moisture resistance and long-term performance are two important factors to consider when assessing the durability of thermal insulation materials.
Moisture Resistance
Moisture can be a significant concern for thermal insulation materials. Exposure to moisture can reduce the effectiveness of the insulation and lead to other issues such as mold growth. Therefore, it is important to choose a material that can resist moisture.
One way to test the moisture resistance of a material is to subject it to a water immersion test. During this test, the material is submerged in water for a specified period of time. After the test, the material is evaluated for any changes in weight or thickness. The results of this test can help determine how well the material will perform in wet environments.
Long-Term Performance
In addition to moisture resistance, it is important to consider the long-term performance of a thermal insulation material. Over time, some materials may degrade or lose their insulating properties. Therefore, it is important to choose a material that will maintain its performance over an extended period of time.
One way to test the long-term performance of a material is to subject it to accelerated aging tests. During these tests, the material is exposed to conditions that simulate long-term exposure to the environment. The material is then evaluated for any changes in weight, thickness, or insulating properties. The results of these tests can help determine how well the material will perform over time.
Overall, durability assessments are an important part of selecting a thermal insulation material. By considering factors such as moisture resistance and long-term performance, you can choose a material that will perform well in a variety of environments.
Environmental and Health Impact
Thermal insulation materials play a crucial role in reducing energy consumption and carbon emissions in buildings. However, they can also have a significant environmental and health impact. In this section, we will discuss the environmental and health impact of different thermal insulation materials.
Eco-Friendly Materials
Eco-friendly thermal insulation materials are becoming increasingly popular due to their low environmental impact. These materials are made from renewable resources and are biodegradable, recyclable, or both. Some of the most common eco-friendly thermal insulation materials include:
- Cellulose insulation: made from recycled paper and treated with fire retardants, cellulose insulation is an excellent eco-friendly option. It has a low embodied energy and can be recycled at the end of its life.
- Sheep wool insulation: sheep wool is a natural, renewable, and biodegradable material that has excellent thermal insulation properties. It is also resistant to fire, pests, and mold.
- Hemp insulation: made from the woody stem of the hemp plant, hemp insulation is a natural, renewable, and biodegradable material. It has excellent thermal insulation properties and is resistant to fire and pests.
Health Hazards Assessment
Some thermal insulation materials can have adverse health effects on humans. These materials can release harmful chemicals or fibers into the air, causing respiratory problems, allergies, and other health issues. Some of the most common hazardous thermal insulation materials include:
- Fiberglass insulation: fiberglass insulation is made from glass fibers and can release airborne particles that can cause respiratory problems and skin irritation. It is also a non-renewable material that has a high embodied energy.
- Polyurethane foam insulation: polyurethane foam insulation is made from petrochemicals and can release harmful chemicals into the air. It is also a non-renewable material that has a high embodied energy.
- Mineral wool insulation: mineral wool insulation is made from rock or slag fibers and can release airborne particles that can cause respiratory problems and skin irritation. It is also a non-renewable material that has a high embodied energy.
It is important to consider the environmental and health impact of thermal insulation materials when selecting the right material for your building. Eco-friendly and non-hazardous materials should be given priority to ensure a sustainable and healthy living environment.