Minimum Ignition Energy Apparatus: Understanding Its Importance in Combustible Dust Testing
If you work in an industry that deals with combustible dust, then you know how important it is to understand the risks involved and take necessary precautions. One of the key parameters that you need to determine is the minimum ignition energy (MIE) of the dust. MIE is the lowest amount of energy required to ignite a dust cloud in air. If the MIE of the dust is low, then even a small spark can cause an explosion.
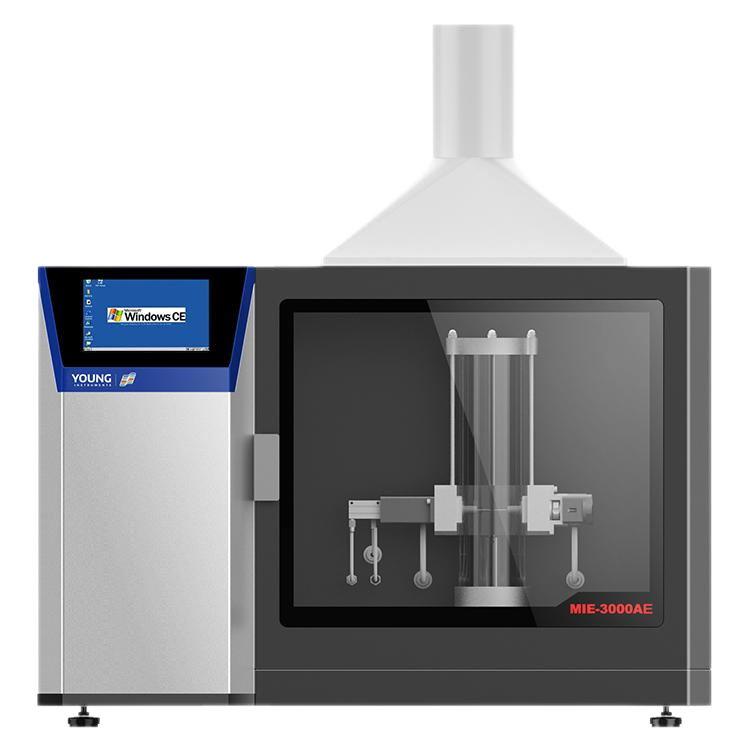
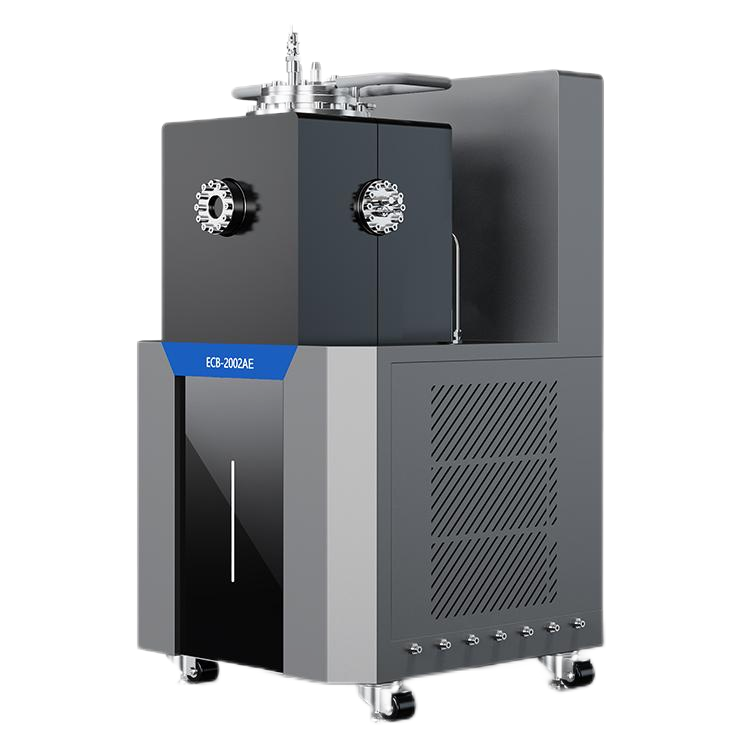
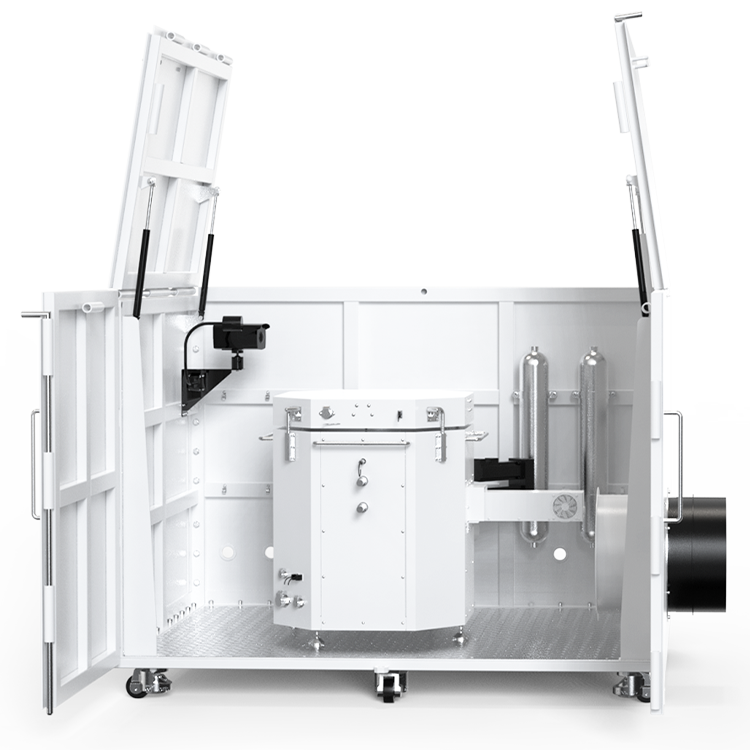
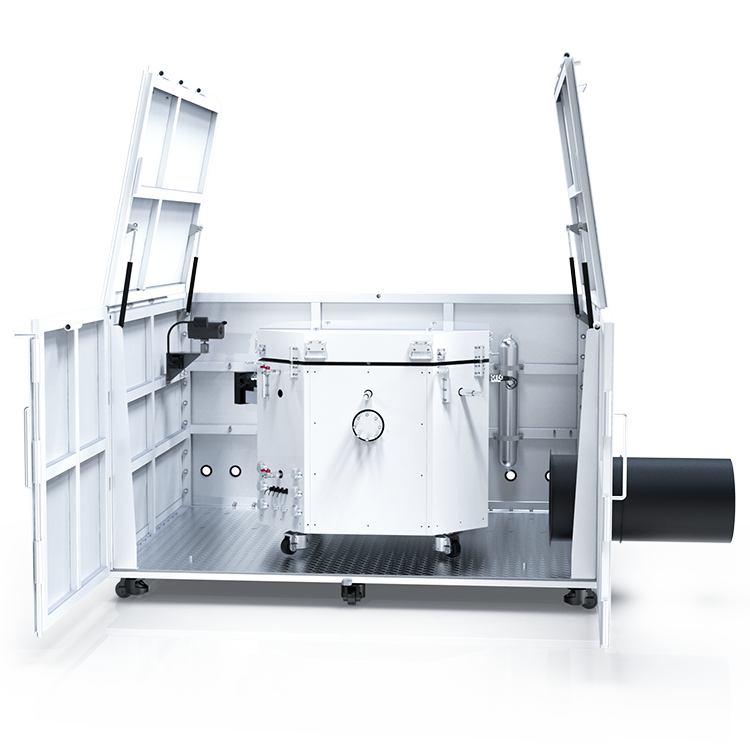
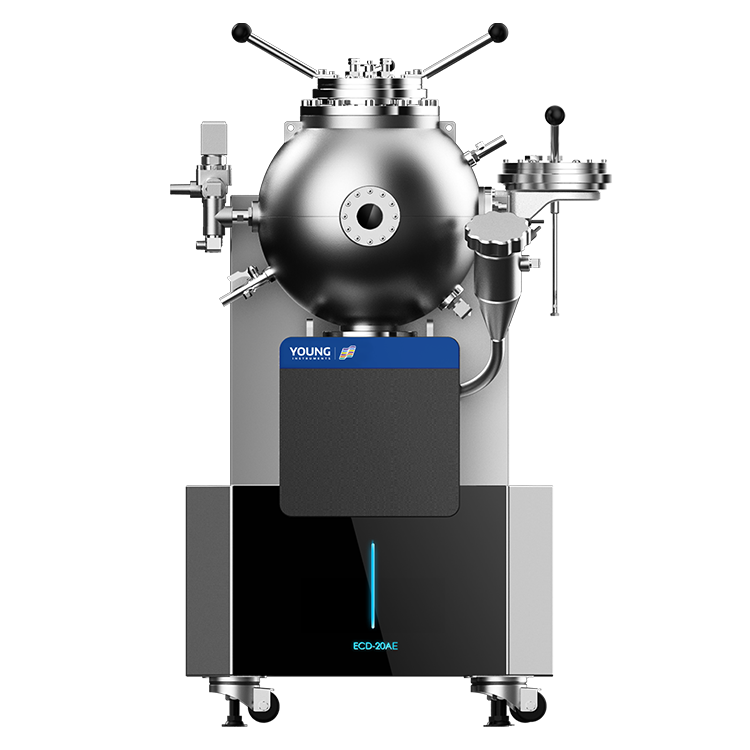
To determine the MIE of a dust, you need a specialized apparatus called the Minimum Ignition Energy Apparatus. This apparatus is designed to simulate the conditions under which a dust explosion can occur and measure the amount of energy required to ignite the dust. The apparatus consists of a tube filled with the dust sample and electrodes that can generate sparks of different energies. By measuring the energy required to ignite the dust sample, you can determine the MIE of the dust.
The MIE value is critical for designing and operating equipment in a safe manner. If the MIE of the dust is known, then engineers can design equipment that will not generate sparks with energy greater than the MIE. This helps to prevent explosions and keep workers safe. In addition, the MIE value can be used to classify the dust according to its explosiveness, which can help in selecting appropriate safety measures.
Fundamentals of Minimum Ignition Energy
The Concept of Ignition Energy
The Minimum Ignition Energy (MIE) is the minimum energy required to ignite a dust cloud under specific conditions. This energy can be supplied by a spark, flame, or other ignition source. The MIE is a critical parameter used to assess the risk of ignition and explosion in industrial processes that handle combustible dusts.
The MIE value depends on several factors, including the dust concentration, particle size distribution, and moisture content. The MIE test involves measuring the energy required to ignite a dust cloud in a test chamber. The test is typically performed using a capacitive discharge spark, which is a high-energy electrical discharge that simulates an ignition source.
Importance in Safety and Industry
The MIE is a critical parameter used in the design and operation of equipment and processes that handle combustible dust. The MIE value is used to determine the level of hazard associated with a particular dust. If the MIE is low, then the dust is more likely to ignite and cause an explosion. Therefore, it is essential to know the MIE value of any dust that is handled in an industrial process.
The MIE value is also used in the selection of electrical equipment that is used in hazardous locations. Electrical equipment that is used in areas where combustible dusts are present must be designed to prevent ignition of the dust. The MIE value is used to determine the level of protection required for electrical equipment in hazardous locations.
In summary, the MIE is a critical parameter used to assess the risk of ignition and explosion in industrial processes that handle combustible dusts. The MIE value is used in the design and operation of equipment and processes that handle combustible dusts and in the selection of electrical equipment that is used in hazardous locations.

Design of MIE Apparatus
Key Components
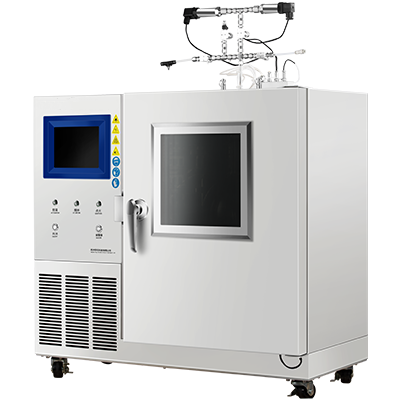
The Minimum Ignition Energy (MIE) apparatus is designed to measure the minimum amount of energy required to ignite a dust or powder. The apparatus consists of a borosilicate glass tube, electrodes, and a power source. The borosilicate glass tube is filled with the dust or powder to be tested and is connected to the electrodes. The electrodes are used to create a spark that ignites the dust or powder. The power source is used to supply the electrodes with the required amount of energy.
Operational Principles
The MIE apparatus works by creating a spark between the electrodes inside the borosilicate glass tube. The energy required to create the spark is gradually increased until ignition occurs. The minimum amount of energy required to ignite the dust or powder is then recorded. The ignition energy is affected by various factors such as the particle size, shape, and concentration of the dust or powder. Therefore, it is important to carefully select the dust or powder used in the test to ensure accurate results.
During the test, the dust or powder is placed inside the borosilicate glass tube and is dispersed evenly. The electrodes are then connected to the power source and the energy is gradually increased until ignition occurs. The minimum ignition energy is then recorded and used to determine the hazard classification of the dust or powder. The MIE apparatus is an important tool in determining the safety of electrical equipment in hazardous locations. It is widely used in industries such as chemical, pharmaceutical, and food processing to ensure the safety of workers and equipment.
Measurement Techniques
When using a Minimum Ignition Energy (MIE) apparatus, there are two main techniques involved: sample preparation and data acquisition and analysis.
Sample Preparation
The first step in MIE testing is to prepare the sample. The sample should be representative of the dust or powder that will be encountered in the actual process. The sample should be dried to a constant weight and sieved to remove any large particles that could interfere with the test.
The sample is then placed into a borosilicate tube, which is then sealed with a rubber stopper. The tube is then purged with nitrogen to remove any oxygen, which could interfere with the test.
Data Acquisition and Analysis
Once the sample is prepared, the MIE apparatus is used to measure the minimum energy required to ignite the sample. The apparatus consists of two electrodes, which are placed at the top of the borosilicate tube.
A high voltage is applied to the electrodes, and the energy required to ignite the sample is measured. The energy is gradually increased until ignition occurs. The energy required to ignite the sample is then recorded.
The data is then analyzed to determine the MIE of the sample. The MIE is the minimum energy required to ignite the sample under the given conditions. The MIE is an important parameter in assessing the risk of dust explosions and in designing explosion prevention and protection systems.
In summary, the MIE apparatus is used to measure the minimum energy required to ignite a dust or powder sample. The sample is prepared by drying and sieving, and then placed into a borosilicate tube. The energy required to ignite the sample is measured using two electrodes, and the data is analyzed to determine the MIE.
Standards and Calibration
International Standards
The Minimum Ignition Energy (MIE) apparatus is used to determine the minimum energy required to ignite a dust cloud in air. The ASTM E2019-99 standard provides a procedure for performing laboratory tests to determine the MIE of a dust cloud. This standard is widely accepted and used in industry for evaluating the spark ignitibility of a dust cloud. The values obtained are specific to the sample tested, the method used, and the test equipment used.
Calibration Procedures
Calibration of the MIE apparatus is essential to ensure accurate and reliable results. Calibration procedures should be performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions and in compliance with relevant international standards. Calibration should be performed at least annually or whenever the apparatus is repaired or modified.
The calibration procedure typically involves measuring the energy required to ignite a standard dust cloud using the MIE apparatus. The energy required should be within a specified range, and the results should be compared to the calibration certificate provided by the manufacturer. Any deviation from the specified range should be investigated and corrected before the apparatus is used for testing.
It is essential to use the correct calibration dust for the MIE apparatus. The calibration dust should be representative of the dust being tested and should have a known MIE value. The calibration dust should be stored in a dry and cool place and should be replaced when it reaches its expiry date.
Regular calibration of the MIE apparatus is essential to ensure accurate and reliable results and to comply with international standards. Calibration procedures should be performed by qualified personnel and in compliance with relevant international standards.