Coal Dust Explosion Test: Understanding the Risks and Safety Measures
Coal dust explosions can be deadly and catastrophic. They occur when coal dust is ignited in a confined space, such as a mine or storage silo, and the resulting pressure wave can cause extensive damage. To prevent these explosions, coal dust explosion tests are conducted to determine the explosibility of coal dust and to develop measures to mitigate the risks.
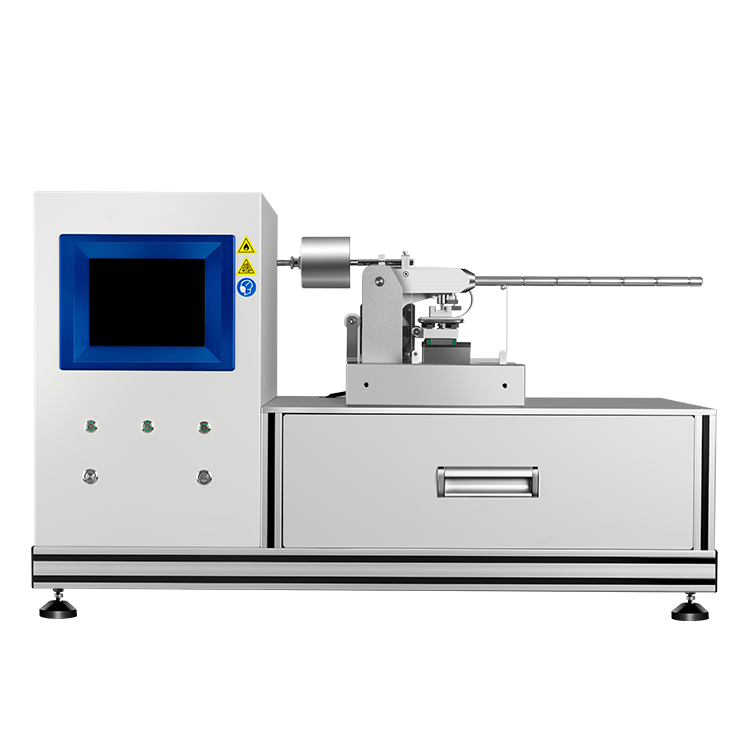
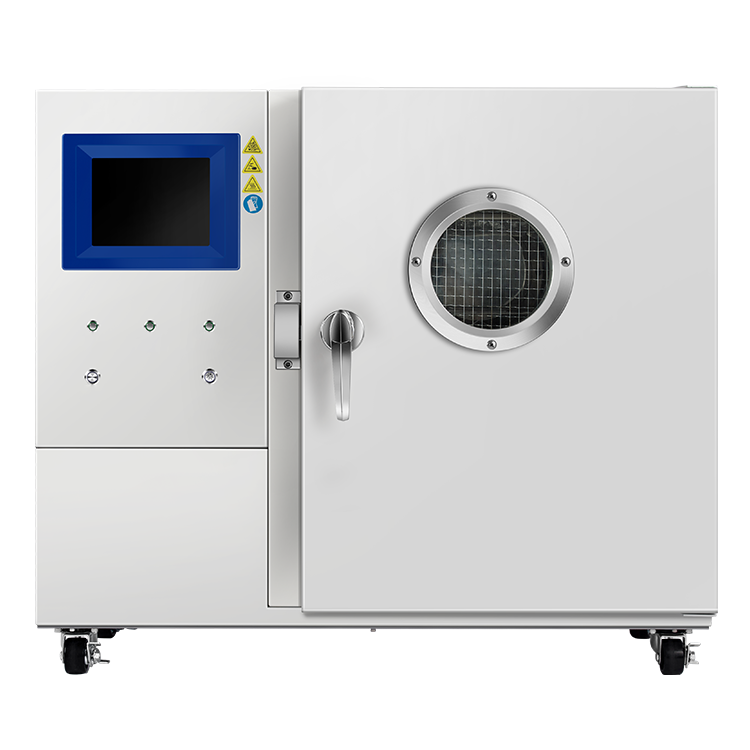
The tests are typically conducted in specialized chambers that simulate the conditions of a coal dust explosion. These chambers are designed to be safe and to contain the explosion, while allowing researchers to measure the pressure, temperature, and other parameters of the explosion. The results of these tests can be used to develop safety guidelines and to design explosion-proof equipment for use in coal mines and other industries that handle coal dust.
Coal dust explosion tests are an important tool for ensuring the safety of workers and facilities that handle coal dust. By understanding the explosibility of coal dust and developing measures to mitigate the risks, we can prevent catastrophic explosions and protect human lives.
Fundamentals of Coal Dust Explosions
Coal dust explosions are a major hazard in the mining and processing industries. Understanding the fundamentals of coal dust explosions is crucial for preventing such accidents. This section will cover the chemistry of coal dust combustion and the conditions necessary for coal dust explosibility.
Chemistry of Coal Dust Combustion
Coal dust is highly combustible and can ignite at temperatures as low as 150°C. When coal dust is suspended in air, it forms a cloud that can ignite and explode if exposed to a spark or flame. The combustion of coal dust is an exothermic reaction that releases heat and produces carbon dioxide, water vapor, and other gases.
The combustion of coal dust can be represented by the following chemical equation:
C + O2 → CO2 + heat
The heat released during the combustion of coal dust can raise the temperature of the surrounding air, causing the coal dust to ignite and explode. The severity of the explosion depends on the amount and concentration of coal dust in the air, as well as the presence of other combustible materials.
Conditions for Coal Dust Explosibility
Coal dust explosions require three conditions: fuel, oxygen, and an ignition source. The fuel is provided by the coal dust, which can be suspended in air and form a combustible cloud. The oxygen is provided by the air, which is necessary for the combustion of the coal dust. The ignition source can be any spark or flame that is hot enough to ignite the coal dust.
The minimum concentration of coal dust in the air that can ignite and cause an explosion is known as the Minimum Explosible Concentration (MEC). The MEC varies depending on the type of coal dust and the size of the particles. For example, subbituminous coal dust has a lower MEC than bituminous coal dust.
Other factors that can contribute to coal dust explosibility include the size and shape of the particles, the moisture content of the coal dust, and the presence of other combustible materials. For example, coal dust that is wet or contains oil can be more prone to ignition and explosion.
In summary, coal dust explosions are a serious hazard in the mining and processing industries. Understanding the chemistry of coal dust combustion and the conditions necessary for coal dust explosibility is essential for preventing such accidents.
Coal Dust Explosion Test Procedures
Sampling and Preparation
In order to conduct a coal dust explosion test, it is important to obtain a representative sample of the coal dust. This sample should be collected in accordance with established procedures and guidelines, and should be representative of the coal dust that will be present in the actual environment where the explosion may occur.
Once the sample has been collected, it must be prepared for testing. This typically involves grinding the coal dust to a specific particle size and mixing it with air or another oxidizing agent to create a test atmosphere. The particle size distribution of the coal dust is an important factor in the explosibility of the dust, and must be carefully controlled during the preparation process.
Standardized Testing Methods
There are several standardized methods for conducting coal dust explosion tests, including the ASTM E1226-19 Standard Test Method for Explosibility of Dust Clouds and the ISO 1928:2009 Standard Test Method for Determination of Hardgrove Grindability Index of Coal. These methods specify the test apparatus, test conditions, and test procedures to be used in order to ensure that the results of the test are accurate and reproducible.
During the test, the coal dust is dispersed in a test chamber and ignited using a spark or other ignition source. The resulting explosion is measured in terms of the maximum pressure and rate of pressure rise, as well as the minimum ignition energy required to initiate the explosion. These parameters are used to evaluate the explosibility of the coal dust and to develop appropriate mitigation strategies to prevent explosions from occurring in real-world settings.
In summary, the coal dust explosion test procedures involve obtaining a representative sample of the coal dust and preparing it for testing, followed by conducting the test using standardized methods and measuring the resulting explosion parameters. By following these procedures, researchers and safety professionals can gain valuable insights into the explosibility of coal dust and develop effective strategies for preventing explosions in industrial settings.
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
Coal dust explosions can be prevented or mitigated through various measures. In this section, we will discuss some of the strategies that can be implemented to reduce the risk of coal dust explosions.
Dust Control Measures
One of the most effective ways to prevent coal dust explosions is to control the amount of coal dust in the air. This can be achieved through various dust control measures, such as:
- Wetting coal to reduce dust generation
- Using dust suppression sprays
- Installing dust collection systems
- Regularly cleaning work areas and equipment
- Using explosion-proof electrical equipment
Implementing these dust control measures can significantly reduce the amount of coal dust in the air and lower the risk of a coal dust explosion.
Explosion Suppression Systems
Another effective strategy for preventing coal dust explosions is to install explosion suppression systems. These systems work by detecting the early signs of an explosion and then releasing a suppressant, such as water or foam, to extinguish the explosion.
Explosion suppression systems can be installed in various parts of the coal handling system, such as coal silos, conveyors, and mills. These systems can help prevent the spread of an explosion and minimize the damage caused by an explosion.
In conclusion, preventing coal dust explosions requires a combination of dust control measures and explosion suppression systems. By implementing these strategies, the risk of a coal dust explosion can be significantly reduced, making the workplace safer for everyone.
Regulatory Framework
Coal dust explosions are a serious hazard in the mining industry, and regulatory frameworks have been established to ensure safety and prevent accidents. This section will discuss the national and international standards that have been put in place to regulate coal dust explosions, as well as the compliance and enforcement mechanisms used to ensure that these standards are met.
National and International Standards
The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) has established several standards related to coal dust explosions, including NFPA 654, which provides guidelines for the prevention of fire and dust explosions from the manufacturing, processing, and handling of combustible particulate solids. Additionally, NFPA 68 and 69 provide guidelines for explosion protection systems and devices, and NFPA 61 provides guidelines for the prevention of fires and explosions in agricultural and food processing facilities.
Internationally, the European Union has established the ATEX directive, which provides guidelines for the prevention of explosions in hazardous environments, including those that involve coal dust. The ATEX directive requires that employers perform a risk assessment and implement measures to prevent explosions, including the use of explosion-proof equipment and the implementation of safe work practices.
Compliance and Enforcement
In order to ensure compliance with national and international standards, regulatory authorities have established mechanisms for enforcement. In the United States, the Mine Safety and Health Administration (MSHA) is responsible for enforcing regulations related to coal dust explosions in the mining industry. MSHA conducts regular inspections of mines and issues citations and fines for violations of safety regulations.
Internationally, the European Union has established a system of conformity assessment, which requires that manufacturers of equipment used in hazardous environments, including those that involve coal dust, comply with the requirements of the ATEX directive. Additionally, the European Union has established a system of notified bodies, which are responsible for certifying that equipment meets the requirements of the ATEX directive.
In conclusion, regulatory frameworks have been established to ensure the safety of workers in the mining industry and prevent coal dust explosions. National and international standards provide guidelines for the prevention of explosions, and compliance and enforcement mechanisms ensure that these standards are met.