Dust Cloud Minimum Ignition Energy Tester: What You Need to Know
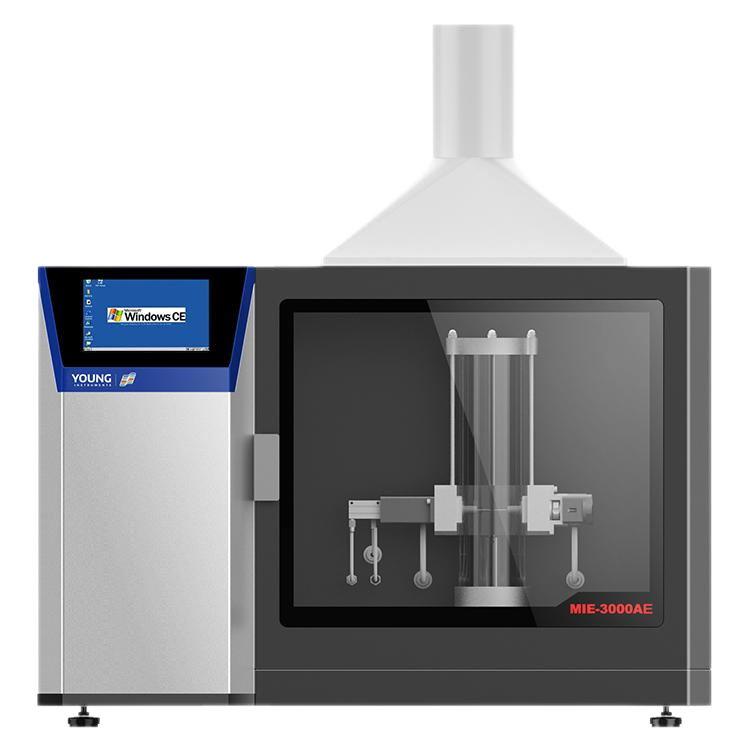
Dust Cloud Minimum Ignition Energy Tester If you work in an industry that involves processing or handling flammable dust, you know how important it is to take every precaution to prevent explosions. One of the most critical steps in preventing dust explosions is to determine the minimum ignition energy (MIE) of the dust cloud. The MIE is the lowest energy level required to ignite a dust cloud and cause an explosion.
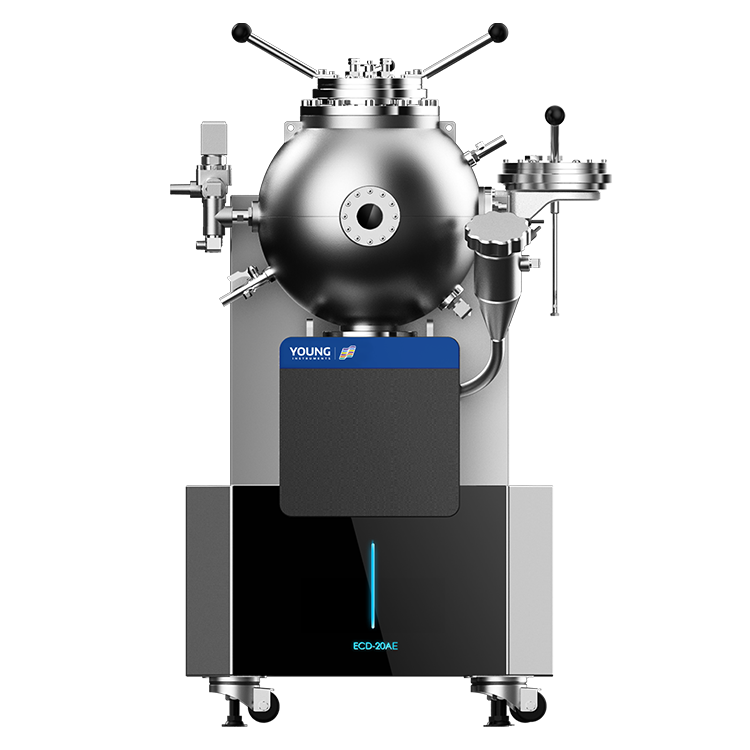
To determine the MIE of a dust cloud, you need a specialized piece of equipment called a Dust Cloud Minimum Ignition Energy Tester. This device measures the spark energy required to ignite a dust cloud in air. The test is conducted by creating a dust cloud in a test chamber and applying a high voltage spark to the cloud. The MIE value is then calculated based on the lowest energy level required to ignite the cloud.
Knowing the MIE of a dust cloud is crucial for assessing the risk of ignition during processing and handling. It allows you to evaluate the need for precautions such as explosion suppression systems, grounding equipment, and other safety measures. By using a Dust Cloud Minimum Ignition Energy Tester, you can ensure that your operations are safe and compliant with industry standards.
Fundamentals of Dust Cloud Ignition
Definition of Minimum Ignition Energy
The minimum ignition energy (MIE) of a dust cloud is the lowest spark energy that can ignite the cloud, measuring the spark ignition sensitivity of a dust cloud [1]. It is an important parameter to consider when designing and operating industrial processes that involve combustible dust. The MIE is determined through testing in a laboratory setting, where the dust is dispersed in a test chamber and a spark is introduced at different energy levels until ignition occurs. The MIE is then recorded as the lowest energy level at which ignition occurred [2].
Importance of Dust Cloud Characterization
Characterizing the properties of dust clouds, including their MIE, is crucial for ensuring the safe operation of industrial processes. Understanding the potential for dust explosions and taking measures to prevent them is essential to protect workers and equipment. The MIE is just one of many parameters that must be considered when evaluating the potential for dust explosions. Other factors, such as dust concentration, particle size, and moisture content, also play a role in determining the likelihood of ignition and the severity of an explosion [3].
In addition to preventing explosions, characterizing dust clouds can also help optimize process efficiency. By understanding the properties of the dust being handled, operators can make informed decisions about equipment design, maintenance, and operation. This can lead to improved process performance, reduced downtime, and increased profitability.
Overall, characterizing dust clouds and determining their MIE is an important step in ensuring safe and efficient industrial processes. By understanding the potential for dust explosions and taking proactive measures to prevent them, operators can protect workers and equipment while optimizing process performance.
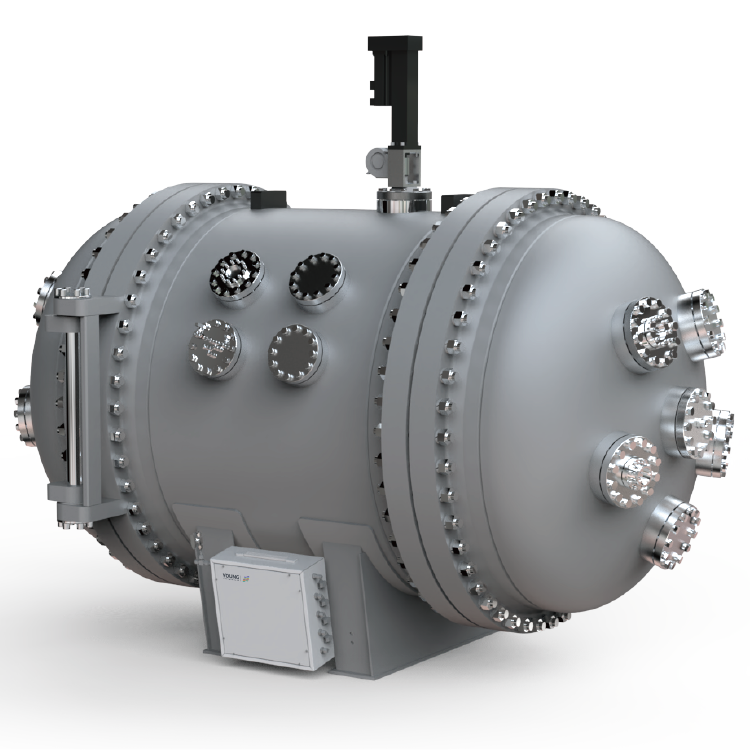
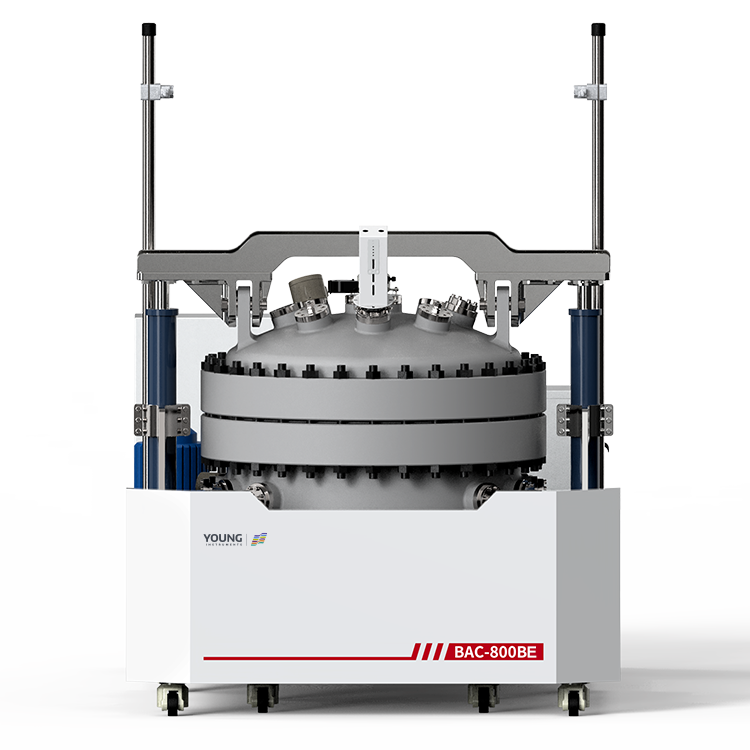
Components of a Dust Cloud Ignition Tester
A Dust Cloud Minimum Ignition Energy Tester consists of three main components: the Ignition Source, Dust Dispersion System, and Testing Chamber.
Ignition Source
The Ignition Source is responsible for providing a high voltage spark that ignites the dust cloud in the Testing Chamber. The spark should be of sufficient energy to ignite the dust cloud, but not so high as to cause an explosion. The spark should also be repeatable, so that multiple tests can be performed with consistent results.
Dust Dispersion System
The Dust Dispersion System is responsible for creating a uniform dust cloud in the Testing Chamber. The system should be capable of dispersing the dust in a controlled manner, so that consistent results can be obtained. The system should also be capable of generating the required dust concentration for the test.
Testing Chamber
The Testing Chamber is where the actual test takes place. The chamber should be designed to prevent any external ignition sources from entering the chamber, and to contain any explosions that may occur. The chamber should also be designed to allow for easy access to the components, so that maintenance and cleaning can be performed easily.
In summary, a Dust Cloud Minimum Ignition Energy Tester consists of an Ignition Source, Dust Dispersion System, and Testing Chamber. The Ignition Source provides a high voltage spark, the Dust Dispersion System creates a uniform dust cloud, and the Testing Chamber is designed to prevent external ignition sources from entering the chamber and to contain any explosions that may occur.
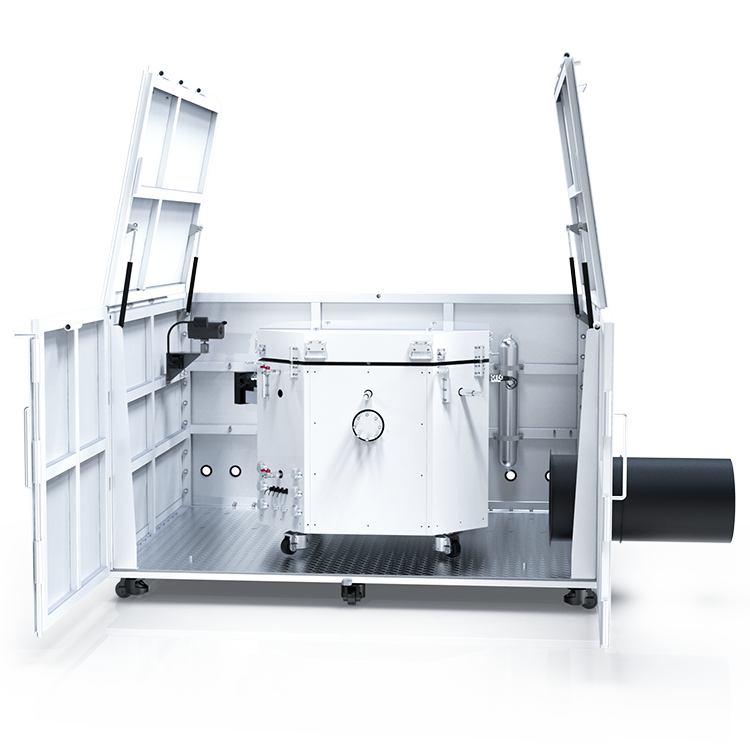
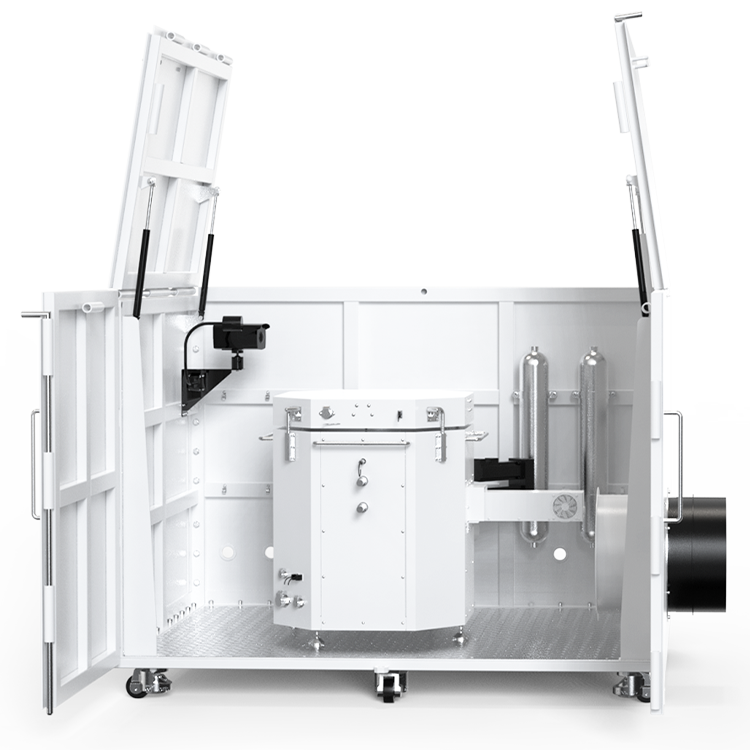
Operational Procedure
Sample Preparation
To prepare the sample for testing, you need to ensure that the material is dry and in its dust form. The sample should be sieved to a specific particle size range. The particle size range is determined by the equipment used for testing. You can use a variety of sieves to achieve the desired particle size range. You should also ensure that the sample is free of any contaminants or impurities that could affect the test results.
Testing Protocols
To begin testing, you need to set up the equipment according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The equipment consists of a test chamber, ignition source, and measurement device. The test chamber is filled with the prepared sample, and the ignition source is introduced into the chamber. The measurement device records the minimum ignition energy required to ignite the sample.
To obtain accurate results, you need to repeat the test several times using different ignition sources and at various locations within the test chamber. The average of the results is then calculated to determine the minimum ignition energy of the sample.
Safety Measures
When working with the Dust Cloud Minimum Ignition Energy Tester, it is essential to follow proper safety measures to prevent accidents and injury. You should wear appropriate personal protective equipment, including gloves, safety glasses, and a lab coat.
You should also ensure that the testing area is well-ventilated to prevent the buildup of flammable gases. It is also important to keep all sources of ignition away from the testing area. Finally, you should follow all safety protocols outlined in the manufacturer’s instructions and guidelines.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
Calculating Ignition Energy
The Dust Cloud Minimum Ignition Energy Tester provides a reliable and accurate method for determining the minimum ignition energy of a dust cloud. This test method involves a high voltage spark that is applied to a dust cloud in a controlled environment. The energy required to ignite the dust cloud is recorded and used to calculate the minimum ignition energy.
The test results are typically reported in millijoules (mJ) and can be used to evaluate the spark ignitibility of a dust cloud. The values obtained are specific to the sample tested, the method used, and the test equipment used. It is important to note that the minimum ignition energy can vary depending on the type of dust, its concentration, and the environmental conditions.
Result Reproducibility
The Dust Cloud Minimum Ignition Energy Tester provides reliable and reproducible results, allowing for accurate assessment of the spark ignitibility of a dust cloud. The test method is standardized and has been validated by industry experts.
To ensure accurate and reproducible results, it is important to follow the recommended test procedures and use properly calibrated equipment. It is also recommended to perform multiple tests on the same sample to ensure consistency and accuracy of the results.
Overall, the Dust Cloud Minimum Ignition Energy Tester provides a reliable and accurate method for determining the minimum ignition energy of a dust cloud. The results obtained can be used to evaluate the spark ignitibility of a dust cloud and assess the likelihood of ignition during processing and handling.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
When it comes to testing for dust cloud minimum ignition energy, regulatory standards and compliance are critical. Companies must ensure that their testing equipment meets industry guidelines and certification processes to avoid safety hazards and legal consequences.
Industry Guidelines
The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) has established guidelines for minimum ignition energy testing, as detailed in Standard Test Method E2019. This test method determines the minimum ignition energy of a dust cloud in air by a high voltage spark. The minimum ignition energy (MIE) of a dust-cloud is primarily used to assess the likelihood of ignition during processing and handling. The likelihood of ignition is used to evaluate the need for precautions such as explosion prevention and control measures.
Certification Processes Dust Cloud Minimum Ignition Energy Tester
To ensure compliance with industry guidelines, companies must use certified equipment that meets ASTM standards. Certification processes involve rigorous testing and evaluation of equipment to ensure that it meets the necessary safety standards. Companies must also ensure that their equipment is regularly inspected and maintained to ensure continued compliance.
In addition to ASTM standards, companies must also comply with relevant Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) regulations. OSHA has established guidelines for the safe handling of combustible dust, including the need for minimum ignition energy testing. Failure to comply with OSHA regulations can result in significant fines and legal consequences.
Overall, regulatory standards and compliance are essential for ensuring the safety of workers and preventing accidents and legal consequences. By following industry guidelines and certification processes, companies can ensure that their testing equipment is safe and effective and that they comply with relevant regulations.