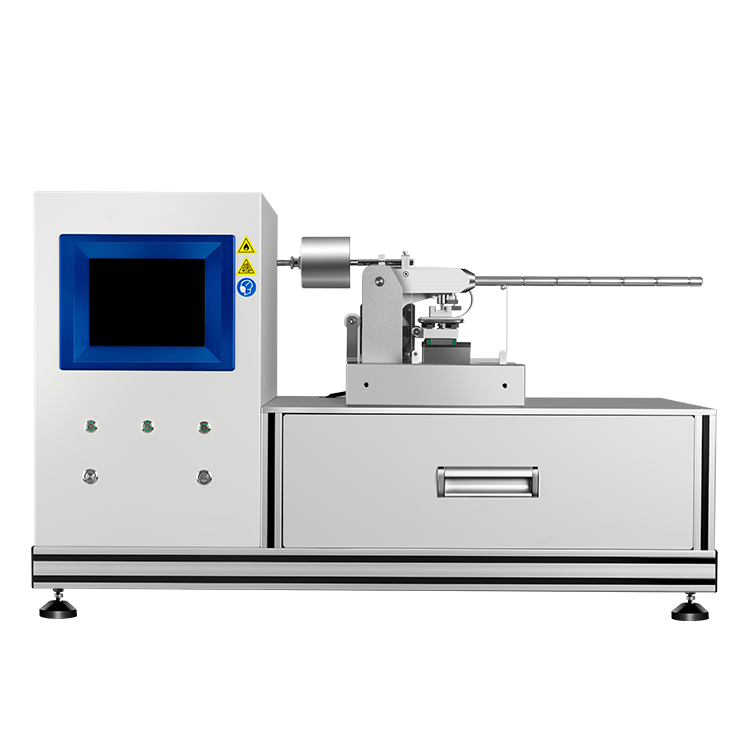
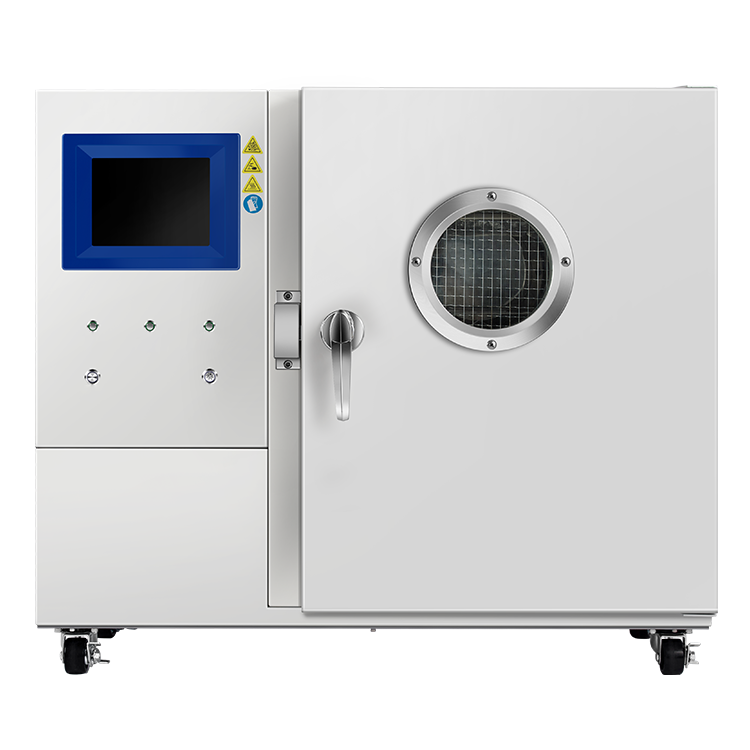
Dust Layer Flammability Testing: Understanding the Basics
Dust layer flammability testing is an essential process that helps to identify the potential fire hazards associated with the handling of combustible dust. The test involves determining the burning behavior of dust layers, which are classified based on their reaction after ignition. The results of the test are used to assess the magnitude of the fire risk associated with the handling of the dust.
Dust layer flammability testing is conducted to determine the minimum ignition temperature of dust layers, which is the lowest temperature at which a hot surface will ignite combustible dust or powders when settled as a dust layer. The test involves placing potentially combustible dust onto an isothermally heated hotplate and forming it into a 12 mm layer. The hotplate is then heated at a constant rate until the dust layer ignites, and the minimum ignition temperature is recorded.
Dust layer flammability testing is crucial for industries that handle combustible dust, such as the chemical, pharmaceutical, and food processing industries. The test helps to identify the fire hazards associated with the handling of the dust and provides valuable information for developing effective safety measures to prevent fires and explosions.
Fundamentals of Dust Layer Flammability
Dust layer flammability testing is an important process used to determine the burning behavior of a dust layer. This type of testing is essential to assess the magnitude of fire risk associated with the handling of dust. In this section, we will explore the fundamentals of dust layer flammability testing, including the chemical and physical properties of dust.
Chemical Properties of Dust
Dust is a complex material that can be composed of a wide range of chemical compounds. The chemical properties of dust can vary depending on the source material and the processing methods used. Some of the common chemical properties of dust that are important for dust layer flammability testing include:
- Ignition temperature: The ignition temperature is the minimum temperature required to ignite a dust cloud or layer. This property is important for determining the fire risk associated with the handling of dust.
- Flash point: The flash point is the temperature at which a substance will ignite when exposed to an ignition source. This property is important for determining the potential for a dust explosion.
- Explosive limits: The explosive limits are the range of concentrations of dust in air that can result in an explosion. This property is important for determining the potential for a dust explosion.
Physical Properties of Dust
In addition to the chemical properties of dust, the physical properties of dust are also important for dust layer flammability testing. Some of the common physical properties of dust that are important for dust layer flammability testing include:
- Particle size: The particle size of dust can affect its flammability and explosiveness. Smaller particles are more likely to ignite and can be more explosive.
- Bulk density: The bulk density of dust can affect its flammability and explosiveness. Dust with a lower bulk density is more likely to ignite and can be more explosive.
- Moisture content: The moisture content of dust can affect its flammability and explosiveness. Dust with a higher moisture content is less likely to ignite and is less explosive.
Overall, understanding the chemical and physical properties of dust is essential for dust layer flammability testing. By assessing these properties, it is possible to determine the fire risk associated with the handling of dust and to take appropriate measures to prevent dust explosions.
Testing Methodologies
Standard Test Procedures
There are several standard test procedures used for dust layer flammability testing. The most commonly used procedures are ASTM E2021 and EN50281. ASTM E2021 identifies dangerous operating temperatures at which a dust layer will self-heat. EN50281-2:1999 is used to determine the minimum ignition temperatures of dust. These tests are designed to simulate a primary dust explosion, secondary dust explosion, and/or dust flash fire.
Sampling and Preparation
When conducting dust layer flammability testing, it is important to take representative samples of the dust layer. The samples should be collected from the top layer of the dust in the area of concern. The samples should be collected in a clean, dry container and analyzed immediately. If the samples cannot be analyzed immediately, they should be stored in a cool, dry place.
Before conducting the tests, the dust samples should be prepared by sieving them to remove any large particles or debris. The samples should then be homogenized to ensure that they are representative of the entire dust layer. The homogenized samples should be placed in a test apparatus and subjected to the appropriate test procedures.
It is important to note that the results of dust layer flammability testing can be affected by a number of factors, including the particle size distribution of the dust, the moisture content of the dust, and the presence of other materials in the dust layer. Therefore, it is important to carefully control these factors when conducting the tests to ensure that the results are accurate and representative of the actual conditions in the area of concern.
Safety Protocols
When conducting Dust Layer Flammability Testing, it is crucial to follow proper safety protocols to prevent accidents and ensure the safety of everyone involved. This section will outline the necessary Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) and Emergency Response Procedures to follow during testing.
Personal Protective Equipment
Wearing the proper PPE is essential to minimize the risk of injury during Dust Layer Flammability Testing. The following PPE is recommended:
- Eye Protection: Safety goggles or a face shield should be worn to protect your eyes from dust particles or any debris that may fly up during testing.
- Respiratory Protection: A respirator should be worn to prevent inhalation of dust particles that may be harmful to your health.
- Gloves: Appropriate gloves should be worn to protect your hands from any sharp objects or hot surfaces.
- Clothing: Wear appropriate clothing that covers your arms and legs to minimize skin exposure.
Emergency Response Procedures
Despite the precautions taken, accidents can still happen during Dust Layer Flammability Testing. It is essential to have an Emergency Response Plan in place to ensure everyone’s safety. The following procedures should be followed in case of an emergency:
- Evacuation: In case of an emergency, evacuate the testing area immediately.
- First Aid: If someone is injured, provide first aid as necessary.
- Fire Extinguisher: Keep a fire extinguisher nearby and make sure everyone knows how to use it.
- Emergency Contacts: Have a list of emergency contacts readily available in case of an accident.
By following these safety protocols, you can ensure a safe and successful Dust Layer Flammability Testing process.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
After conducting Dust Layer Flammability Testing, it is important to analyze and interpret the results to determine the potential fire and explosion hazards of the dust in question. This section will cover two important aspects of data analysis and interpretation: statistical relevance and result reproducibility.
Statistical Relevance
When analyzing the results of Dust Layer Flammability Testing, it is important to determine if the results are statistically relevant. This means that the data collected is representative of the entire sample and can be used to make accurate predictions about the behavior of the dust in question.
One way to determine statistical relevance is to calculate the standard deviation of the results. A low standard deviation indicates that the results are tightly clustered around the mean, while a high standard deviation indicates that the results are more spread out. In general, a standard deviation of less than 10% is considered statistically relevant.
Another way to determine statistical relevance is to conduct a t-test. A t-test compares the mean of two samples to determine if they are significantly different from each other. If the p-value of the t-test is less than 0.05, then the results are statistically relevant.
Result Reproducibility
In addition to statistical relevance, it is important to ensure that the results of Dust Layer Flammability Testing are reproducible. This means that if the test were to be repeated, the results would be similar.
To ensure result reproducibility, it is important to follow a standardized testing protocol and use calibrated equipment. It is also important to conduct multiple tests and compare the results to ensure consistency.
In conclusion, analyzing and interpreting the results of Dust Layer Flammability Testing is crucial for determining the potential fire and explosion hazards of a particular dust. By ensuring statistical relevance and result reproducibility, you can make accurate predictions about the behavior of the dust and take appropriate safety measures to prevent accidents.
Regulatory Framework
When it comes to dust layer flammability testing, there are several national and international standards and guidelines that you should be aware of. Understanding these regulations is crucial to ensure that you are following the proper procedures and protocols to keep your workplace safe.
National Standards
In the United States, the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) has developed several standards related to dust layer flammability testing. The most important of these is NFPA 652, which provides a comprehensive approach to managing combustible dust hazards in the workplace. Other relevant standards include NFPA 68, 69, 70, 61, 484, 664, and 654.
The International Fire Code (IFC) is another important national standard that outlines regulations for dust explosion protection. According to the IFC Chapter 22 statement on dust explosion protection, “the fire code official is authorized to enforce provisions of codes and standards listed in Table 2204.1 to prevent and control dust explosions.” The listed standards are the NFPA standards described above.
International Guidelines
On the international level, the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has developed several standards related to dust layer flammability testing. These include IEC 60079-20-1, which outlines the requirements for the testing and assessment of equipment that is used in explosive atmospheres, and IEC 61241-1, which provides guidance on the selection, installation, and maintenance of electrical equipment in hazardous areas.
The European Union (EU) has also developed regulations related to dust layer flammability testing. The ATEX Directive (2014/34/EU) outlines the requirements for equipment and protective systems intended for use in potentially explosive atmospheres. The directive applies to all equipment that is used in explosive atmospheres, including electrical and non-electrical equipment.
It is important to note that these regulations and guidelines are subject to change, so it is essential to stay up-to-date with the latest developments in the field. By following these regulations and guidelines, you can help ensure that your workplace is safe and free from the risks associated with combustible dust hazards.