Flammable Limits Tester: Understanding Its Importance in Industrial Settings
If you work with flammable substances, it is crucial to know their flammable limits. The lower flammable limit (LFL) and upper flammable limit (UFL) define the concentration range of a gas or vapor that can ignite and burn in the presence of an ignition source. Operating outside of these safe concentration limits can lead to catastrophic consequences, including fires and explosions.
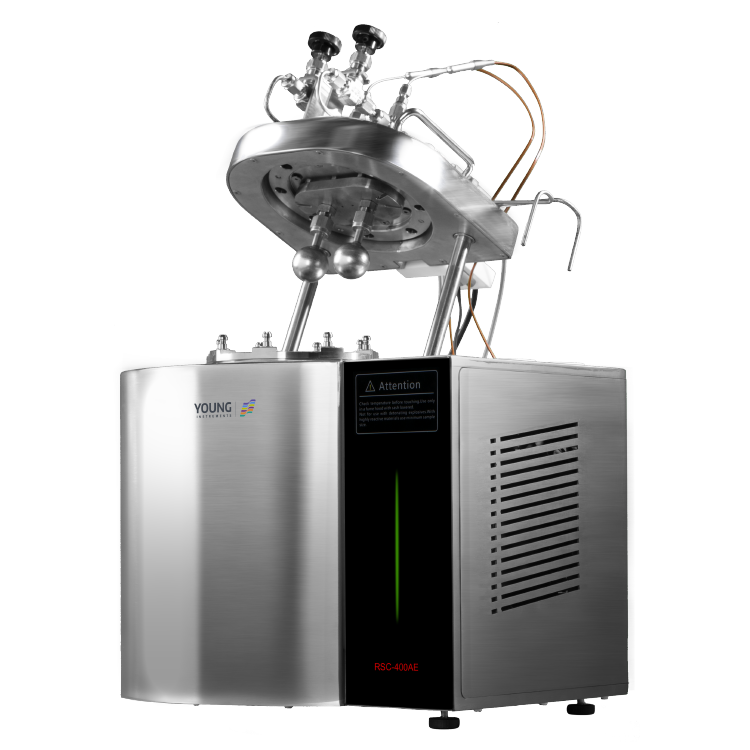
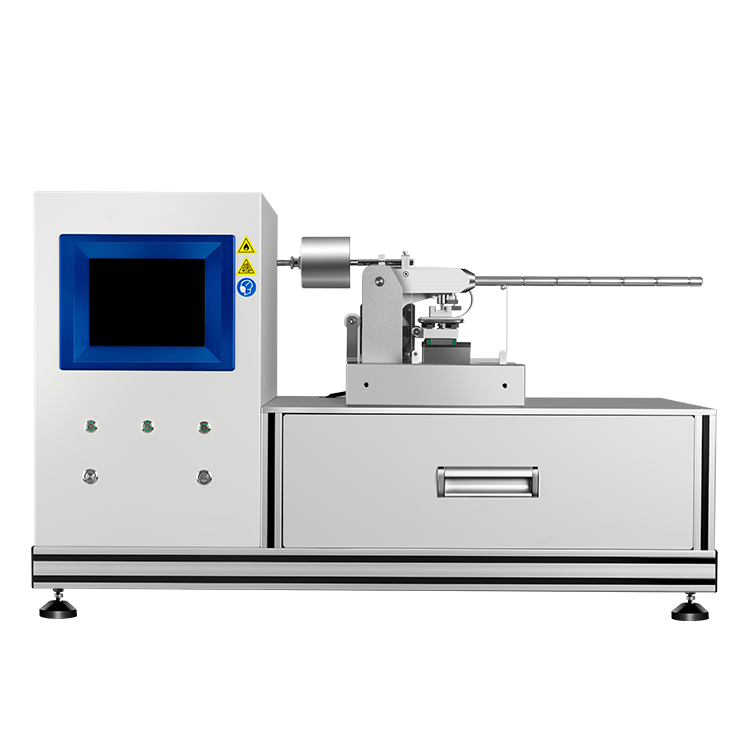
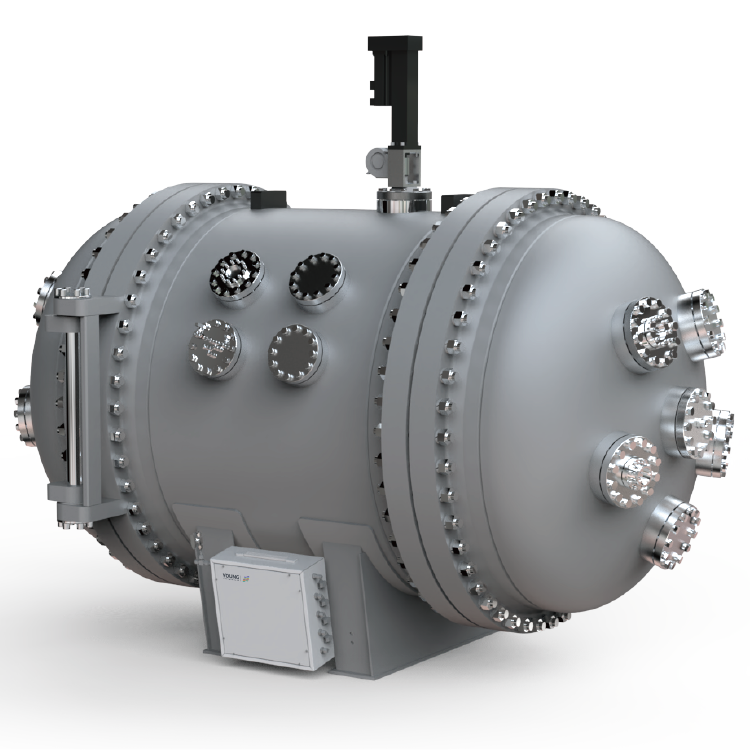
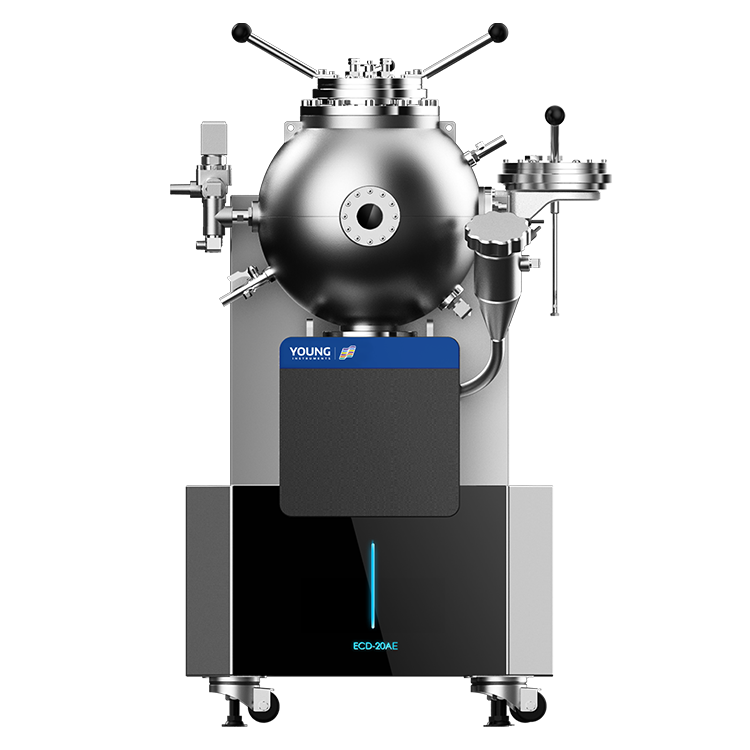
To prevent such accidents, you need a reliable way to determine the LFL and UFL of your flammable materials. This is where a flammable limits tester comes in. A flammable limits tester is a specialized device that measures the concentration range of a gas or vapor that can ignite and burn. By providing accurate and repeatable results, a flammable limits tester helps you ensure that your flammable materials are handled and stored safely.
There are different types of flammable limits testers available, each designed for specific applications. Some testers are used for laboratory testing, while others are suitable for field testing. Some testers measure the LFL and UFL of combustible gases and vapors, while others measure the minimum ignition energy (MIE) or the autoignition temperature (AIT) of flammable materials. Choosing the right flammable limits tester for your needs depends on factors such as the type of material you are testing, the testing environment, and the required accuracy of the results.
Fundamentals of Flammable Limits Testing
If you work with flammable gases or liquids, it is important to understand the flammable limits of these substances. Flammable limits are the range of concentrations in which a substance can ignite and burn. The lower flammable limit (LFL) is the minimum concentration of a substance in air that can ignite and burn. The upper flammable limit (UFL) is the maximum concentration of a substance in the air that can ignite and burn.
To determine the flammable limits of a substance, you need to conduct flammability testing. Flammability testing involves exposing a substance to a range of concentrations of air and measuring its flammability. The most common flammability testing method is the ASTM E681 test method. This method determines the LFL and UFL of a substance by measuring the concentration of the substance in the air at which it ignites and burns.
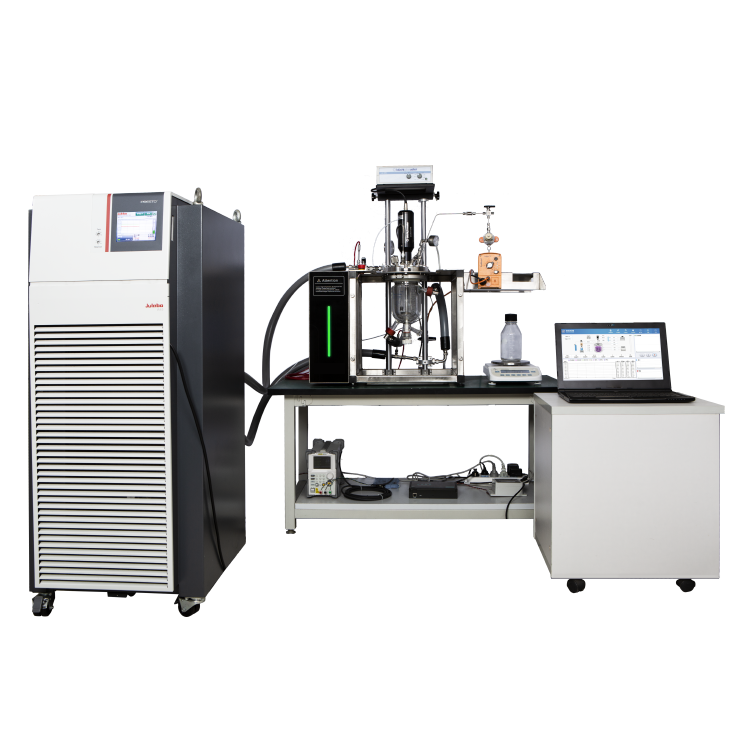
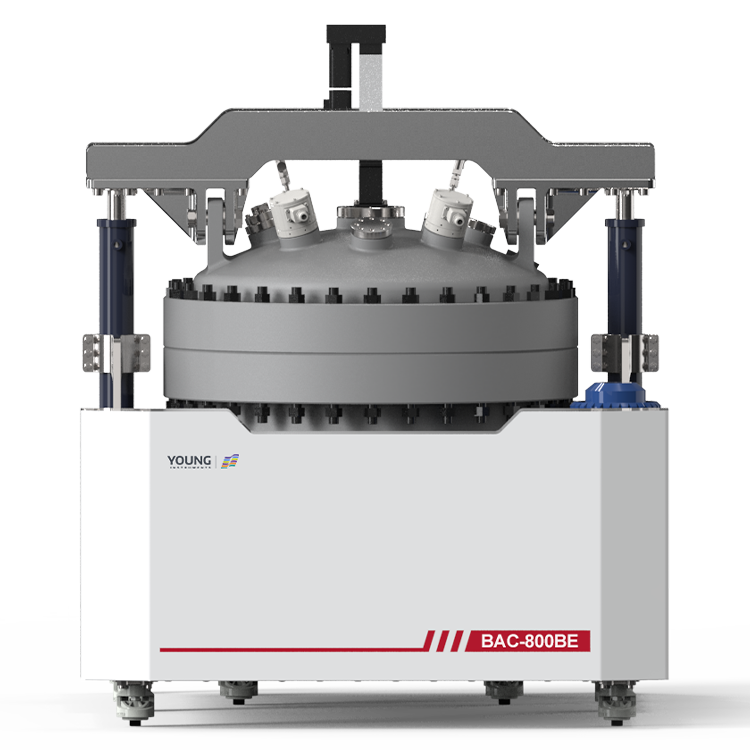
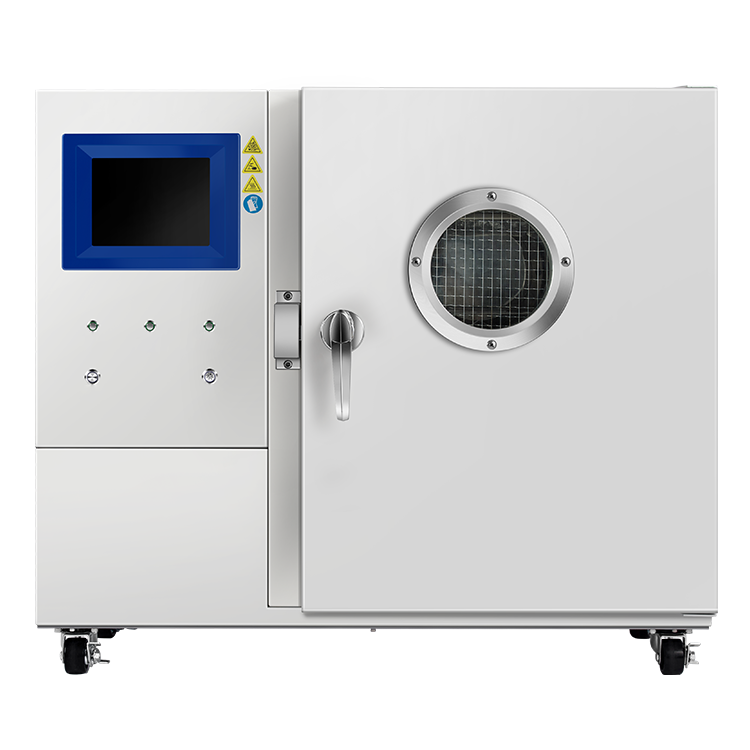
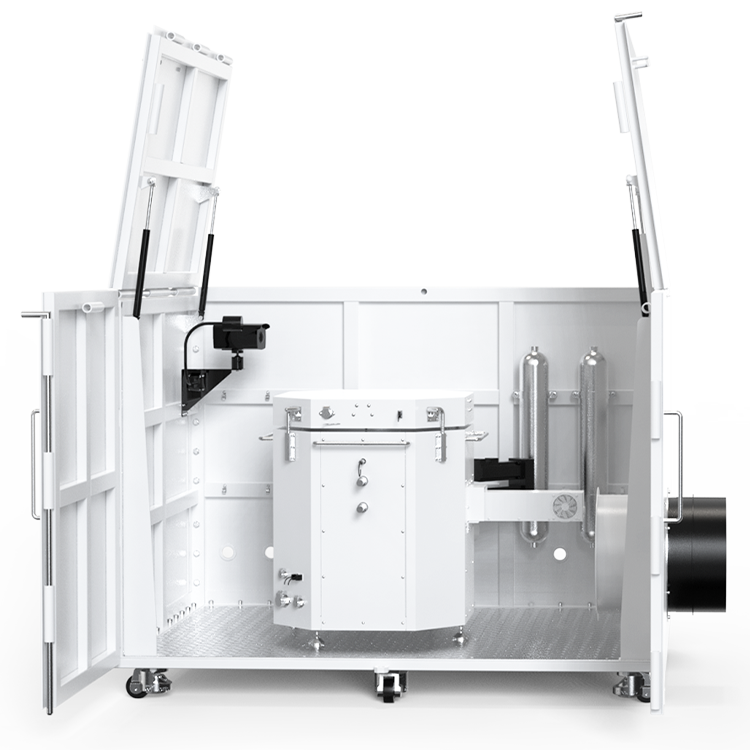
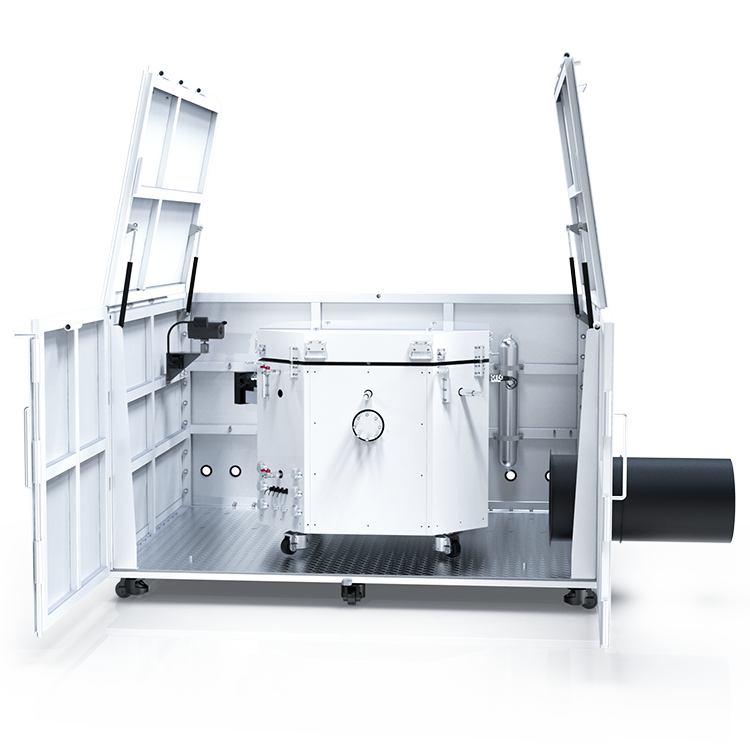
During flammability testing, a Flammable Limits Tester is used to measure the concentration of a substance in air. The tester consists of a chamber in which a mixture of the substance and air is introduced. The concentration of the substance is gradually increased until it reaches the LFL and UFL. The tester then measures the concentration of the substance at which it ignites and burns.
Flammability testing is important for ensuring the safety of workers and equipment. By knowing the flammable limits of a substance, you can determine the safe operating range for the substance. This information is critical for developing safe handling and storage procedures and for preventing accidents and fires.
Design and Operation of Flammable Limits Testers
Safety Features
When it comes to flammable limits testers, safety is of the utmost importance. These devices are designed to measure the lower and upper concentration limits of flammability of chemicals that have sufficient vapor pressure to form flammable mixtures in air at atmospheric pressure at the test temperature. As such, they must be equipped with various safety features to prevent accidents.
One of the most important safety features of a flammable limits tester is the ignition protection system. This system prevents any sparks or flames from igniting the flammable vapor inside the testing chamber. It typically includes explosion-proof electrical components, grounded metal casings, and a ventilation system that removes any flammable vapors from the testing chamber.
Another important safety feature is the emergency shut-off system. This system allows you to quickly shut down the tester in case of an emergency. It typically includes a large, easily accessible button that, when pressed, cuts off power to the tester and activates an alarm to alert nearby personnel.
Control Systems
Flammable limits testers are typically equipped with advanced control systems that allow you to precisely control the testing conditions. This is important because even slight variations in temperature, pressure, or humidity can affect the flammability limits of a chemical.
One important component of the control system is the temperature controller. This device allows you to set the temperature of the testing chamber to a precise degree and maintain it throughout the testing process. It typically includes a digital display that shows the current temperature and allows you to adjust it as needed.
Another important component is the pressure control system. This system allows you to set the pressure of the testing chamber to a precise level and maintain it throughout the testing process. It typically includes a pressure gauge that shows the current pressure and allows you to adjust it as needed.
Finally, the humidity control system is also important. This system allows you to set the humidity of the testing chamber to a precise level and maintain it throughout the testing process. It typically includes a digital display that shows the current humidity and allows you to adjust it as needed.
Overall, flammable limits testers are sophisticated devices that require careful design and operation to ensure accurate and safe testing. By understanding the safety features and control systems of these devices, you can ensure that you are using them properly and obtaining reliable results.
Standards and Compliance
When it comes to flammable limits testers, it’s important to ensure that the device you are using meets the appropriate standards and regulations. This will ensure that your testing is accurate and reliable, and that your results will be accepted by regulatory bodies.
ASTM Standards
The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) has developed a number of standards related to flammability testing. One of the most commonly used is ASTM E681-09, which outlines the standard test method for concentration limits of flammability of chemicals. This standard specifies the procedure for determining the lower and upper flammable limits of a gas or vapor in air at room temperature and atmospheric pressure.
Another important ASTM standard is ASTM E1209-05, which covers the standard test method for fire-test-response of upholstered furniture using a bench scale oxygen consumption calorimeter. This test method is used to determine the fire-test-response characteristics of upholstered furniture and mattresses under specified ignition sources.
ISO/IEC Regulations
In addition to ASTM standards, there are also a number of regulations from the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) that relate to flammability testing. One of the most important is ISO 12136:2011, which specifies a test method for determining the burning behavior of vertically oriented specimens of textiles and industrial products in response to a small open flame.
Another key regulation is IEC 60695-2-11:2015, which specifies the test method for the flammability of materials used in electronic and electrical equipment. This standard provides a means of determining the flammability characteristics of materials used in electronic and electrical equipment, and is often used by manufacturers to ensure that their products meet safety standards.
By ensuring that your flammable limits tester meets these standards and regulations, you can be confident that your testing is accurate and reliable. This will help you to make informed decisions about the safety of materials and products, and ensure that you are in compliance with relevant regulations.
Testing Procedures
Sample Preparation
Before conducting the Flammable Limits Test, proper sample preparation is essential. The sample must be collected and stored in a container that is free from any contamination. The container must be airtight to prevent any leakage or evaporation of the sample. The sample size should be sufficient to ensure accurate test results.
Test Execution
The Flammable Limits Test is conducted by introducing the sample into a test chamber and gradually increasing the concentration of the sample until the lower flammable limit (LFL) is reached. The LFL is the minimum concentration of the sample in air that can ignite and propagate a flame.
During the test, the temperature and pressure of the test chamber are monitored to ensure that they remain within the specified range. The test is repeated several times to ensure the accuracy of the results. The upper flammable limit (UFL) is also determined in a similar manner.
Once the LFL and UFL are determined, the explosivity range can be calculated. The explosivity range is the range of concentrations of the sample in air that can ignite and propagate a flame. This information is important for determining safe operating, storage, and handling procedures for the sample.
In summary, proper sample preparation and accurate test execution are critical for obtaining reliable results in the Flammable Limits Test. By following the appropriate testing procedures, you can ensure that your sample is tested accurately and safely.
Data Interpretation and Analysis
After conducting a flammable limits test using a Flammable Limits Tester, the next step is to interpret and analyze the data obtained. The flammability limits depend on the test temperature and pressure. This test method is limited to an initial pressure of the local ambient or less, with a practical lower pressure limit of approximately 13 kPa (100 mm Hg). The maximum practical operating temperature of this equipment is approximately 150°C.
One way to analyze the data is to plot the concentration of the test substance against the temperature or pressure. This can help identify the Lower Flammable Limit (LFL) and Upper Flammable Limit (UFL) of the substance. The LFL is the minimum concentration of the substance in air that can support combustion, while the UFL is the maximum concentration above which combustion cannot occur.
Another way to analyze the data is to calculate the flammability range, which is the difference between the LFL and UFL. This range provides important information about the safety of handling and storing the substance. If the range is narrow, it means that the substance is highly flammable and requires special precautions to prevent ignition. On the other hand, if the range is wide, it means that the substance is less flammable and can be handled and stored more safely.
It is important to note that the flammability limits depend on several factors, such as the composition of the substance, the temperature, and the pressure. Therefore, it is essential to conduct the test under controlled conditions and to compare the results with published data for similar substances. This will help ensure the accuracy and reliability of the results.
In summary, interpreting and analyzing the data obtained from a Flammable Limits Tester is crucial for understanding the flammability characteristics of a substance and for ensuring its safe handling and storage. By plotting the concentration of the substance against the temperature or pressure, calculating the flammability range, and comparing the results with published data, you can obtain valuable information about the substance and take appropriate safety measures.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
To ensure the proper functioning of your Flammable Limits Tester, it is important to perform regular maintenance. Here are some tips to keep your tester running smoothly:
-
Calibration: The Flammable Limits Tester should be calibrated at least once a year to ensure accurate results. You can either send it to the manufacturer for calibration or use a certified calibration gas to calibrate it yourself.
-
Cleaning: Regular cleaning of the tester is important to prevent contamination and ensure accurate results. Use a soft cloth to wipe down the exterior of the tester and a mild detergent solution to clean the interior.
-
Inspection: Regular inspection of the tester is important to identify any signs of wear and tear. Check the hoses, fittings, and valves for any signs of damage or leaks. Replace any damaged parts immediately to prevent any accidents.
If you encounter any issues with your Flammable Limits Tester, here are some troubleshooting tips:
-
No Reading: If your tester is not giving any reading, check the gas supply and make sure it is properly connected. Also, check the hoses and fittings for any leaks.
-
Inaccurate Reading: If your tester is giving inaccurate readings, check the calibration and make sure it is up to date. Also, check the hoses and fittings for any leaks.
-
Error Messages: If your tester is displaying error messages, refer to the user manual for troubleshooting tips. If the issue persists, contact the manufacturer for assistance.
By following these maintenance and troubleshooting tips, you can ensure the proper functioning of your Flammable Limits Tester and prevent any accidents.