Open Cup vs. Closed Cup Flash Point Testers: What You Need to Know
Evaluating the fire hazards posed by liquids, particularly within industries that handle petroleum, chemicals, aviation, and aerospace materials, relies heavily on the determination of their flash point, a critical metric in this context. The flash point designates the lowest temperature at which a liquid releases a sufficient quantity of combustible vapor capable of igniting upon exposure to a flame under strictly defined conditions.
Gaining an in-depth understanding of the flash point of different substances and precisely determining it plays a vital role in safeguarding processes related to the handling, storage, and transportation of such liquids. In the following discussion, we delve into the nature of flash point testing, distinguish between the methodologies employed by open cup and closed cup flash point testers, and elucidate the significance of this testing within various industries.
Varieties of Flash Point Tester
When examining flash point tester, it is important to distinguish between the two primary types: open cup and closed cup testers. Each of these testing methodologies offers unique characteristics and is suited to different applications based on the properties of the liquid being tested.
Open Cup Flash Point Tester
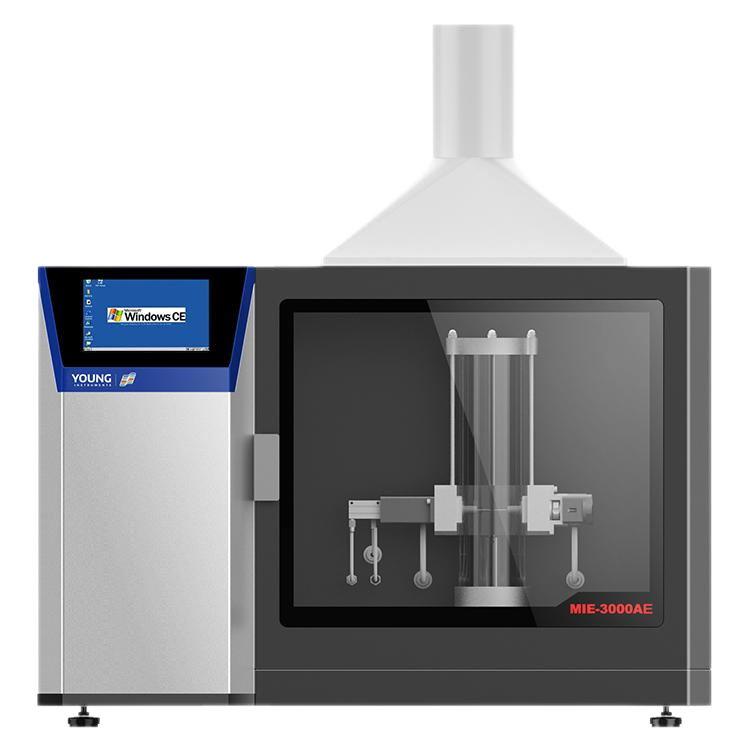
An open cup flash point tester operates by heating a liquid placed in an open container, where the vapor is allowed to interact freely with the surrounding air. Periodic exposure to a flame determines the point at which the vapor ignites, and this temperature is noted as the open cup flash point.
Applications of Open Cup Testers
The open cup method is typically employed for testing heavier oils and lubricants that contain minimal volatile components. These materials, which are stable under ordinary conditions, do not readily produce combustible vapors. The open design of the test setup permits vapor dispersion into the atmosphere, making this approach especially suitable for testing materials less likely to ignite at lower temperatures, such as heavy petroleum products and lubricating oils.
Open Cup Measurement Method
In an open cup flash point test, the liquid under evaluation is poured into an open container, and the temperature is incrementally increased through external heating. As the liquid heats up, it starts releasing vapor into the surrounding air. At predefined intervals, a flame is introduced to the vapor to determine the precise temperature at which it ignites, marking the liquid’s flash point in the open cup configuration.
Limitations of Open Cup Testing
While open cup testing is advantageous for assessing heavier oils, it is less suitable for materials with high volatility. Lighter substances require more controlled testing conditions to prevent vapor dissipation, which could skew the results. Furthermore, the open design of the tester exposes the vapor to potential external factors, such as air currents, which can introduce inconsistencies in the measurement process.
Closed Cup Flash Point Tester
In contrast, closed cup flash point tester is designed to measure the flash points of highly volatile substances such as transformer oils, fuels, and solvents. The testing liquid is enclosed in a sealed container, ensuring that the vapor accumulates in a controlled environment. The container is only opened when the ignition source is introduced, ensuring that the measurement is precise and that no vapor escapes.
Applications of Closed Cup Testers
Closed cup testers are particularly suited to materials that contain lighter components, which vaporize quickly and pose a higher fire risk at lower temperatures. Substances such as transformer oils, fuels, and solvents are commonly tested using this method, especially in industries where high levels of safety are required, such as aerospace and chemical manufacturing.
Closed Cup Measurement Method
During closed cup testing, the sample is enclosed in a container, and the temperature is gradually increased while keeping the container sealed. When the liquid reaches a critical temperature, the vapors it generates are briefly exposed to a flame or ignition source. The closed environment ensures that the vapor is retained for accurate flash point measurement. Because the vapor is allowed to accumulate in the enclosed space, the flash point in a closed cup test is generally lower than in an open cup test, reflecting real-world conditions more accurately.
Advantages of Closed Cup Testing
Closed cup flash point testing is widely regarded for its high level of precision and consistency, making it especially valuable when dealing with materials that present significant fire hazards. The closed design prevents the vapor from dispersing, offering more reliable results. Additionally, this method better simulates real-world conditions, as many combustible materials are stored and transported in sealed containers, emphasizing the relevance of closed cup tests in practical applications.
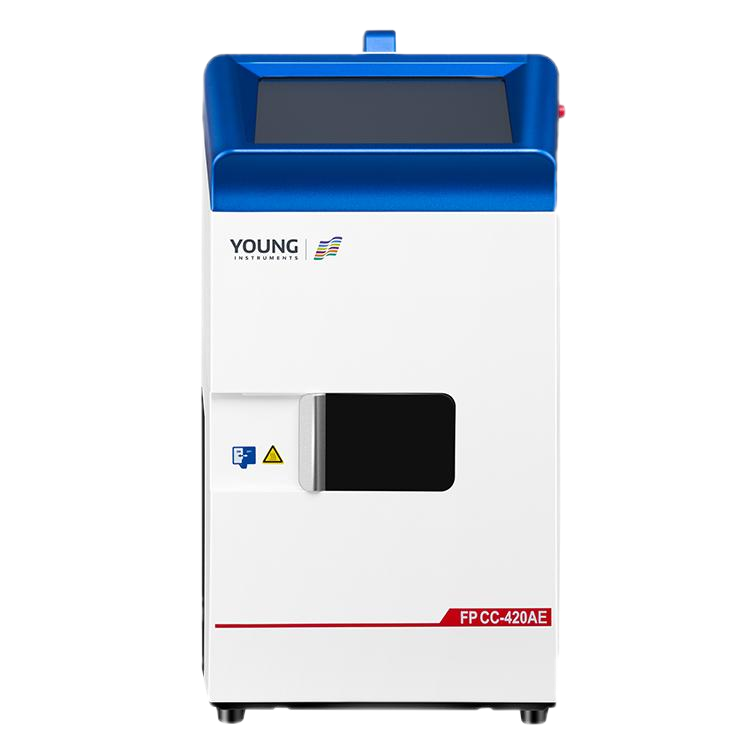
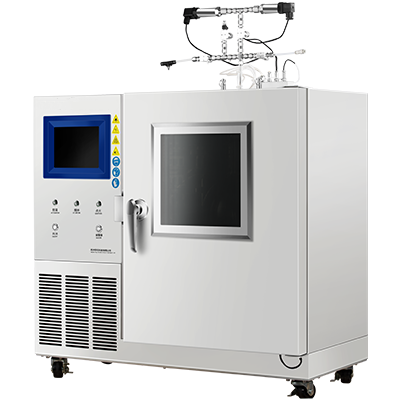
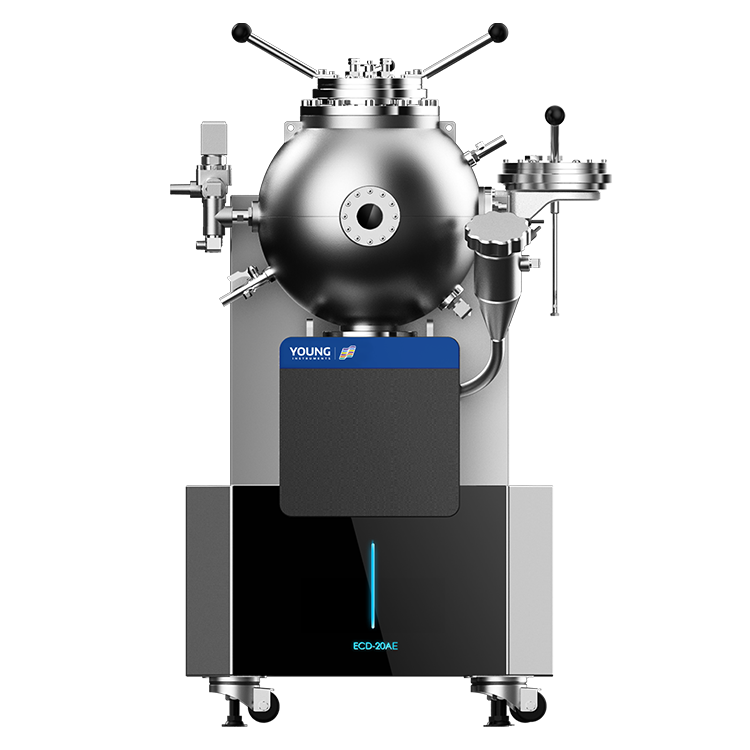
The FP CC-420AE Microscale Continuously Closed Flash Point Tester: A Technological Leap
What Constitutes Flash Point Testing? Flash point testing serves as a diagnostic tool designed to assess the fire hazard characteristics intrinsic to flammable and combustible liquids. This method revolves around identifying the precise temperature at which these liquids emit enough vapors to ignite momentarily when exposed to an ignition source, thereby providing a quantitative measure of their volatility. Flash point testing delivers critical insights that contribute to formulating safety protocols, which are particularly valuable in industries where the manipulation of volatile and combustible materials is a routine aspect of operations.
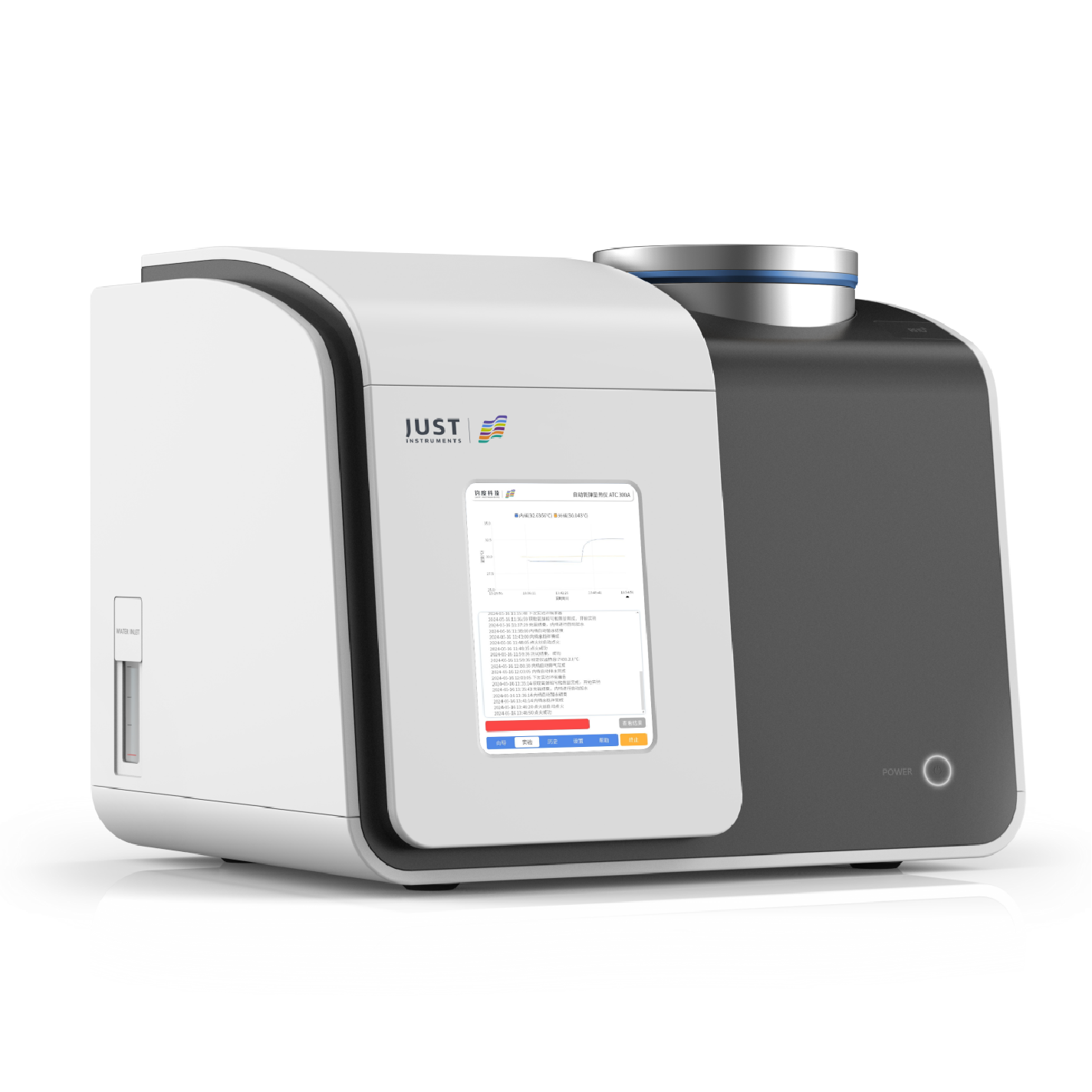
One particularly advanced instrument in the realm of flash point testing is the FP CC-420AE Microscale Continuously Closed Flash Point Tester. This cutting-edge equipment employs the continuous closed cup method, offering superior precision and efficiency in determining the flash points of a wide range of materials, including petroleum products, transformer oils, and substances with high viscosity.
Features and Advantages
The FP CC-420AE boasts several innovative features that distinguish it from other flash point testers:
Small sample requirement: This instrument requires only minimal liquid samples for each test, making it an economical and environmentally friendly option.
Enhanced safety: By operating with a continuously closed system and no open flame, the tester ensures a highly secure testing process.
Refrigerating module: Equipped with an integrated refrigerating module, the tester can handle a broad range of flash point tests while minimizing the time needed for cooling between experiments.
Full automation: The FP CC-420AE automates the entire process, from test initiation to result calibration, delivering consistent, accurate outcomes with minimal operator input.
Real-time data display: The instrument features a 7-inch color touchscreen that shows real-time temperature and pressure data, offering enhanced transparency and control during testing.
Application Versatility
The FP CC-420AE can be applied across various sectors:
Petroleum and fuel testing: The instrument is perfectly suited for determining the flash points of a variety of petroleum products, ensuring compliance with stringent safety regulations.
Lithium battery electrolytes: By measuring the flash point of electrolytes in lithium batteries, the tester helps reduce fire risks and improve battery safety standards.
Industrial oils and chemicals: The tester provides accurate flash point data for high-viscosity materials, including plasticizers and preservatives, making it a valuable tool in industrial manufacturing.
Conclusion
Flash point testing stands as a fundamental component of safety protocols in industries handling flammable and combustible liquids. Whether performed using open cup or closed cup methods, the results from these tests are instrumental in reducing the fire and explosion hazards inherent to volatile materials. Advanced devices like the FP CC-420AE Microscale Continuously Closed Flash Point Tester represent significant technological advancements in this field, offering unparalleled precision, automation, and safety.
By integrating flash point testing into their safety procedures, industries can better protect both their personnel and their assets from the dangers posed by fire hazards, ensuring secure operations across all stages of handling, storage, and transportation.