Heat Flow Meter Instrument: Understanding Its Function and Applications
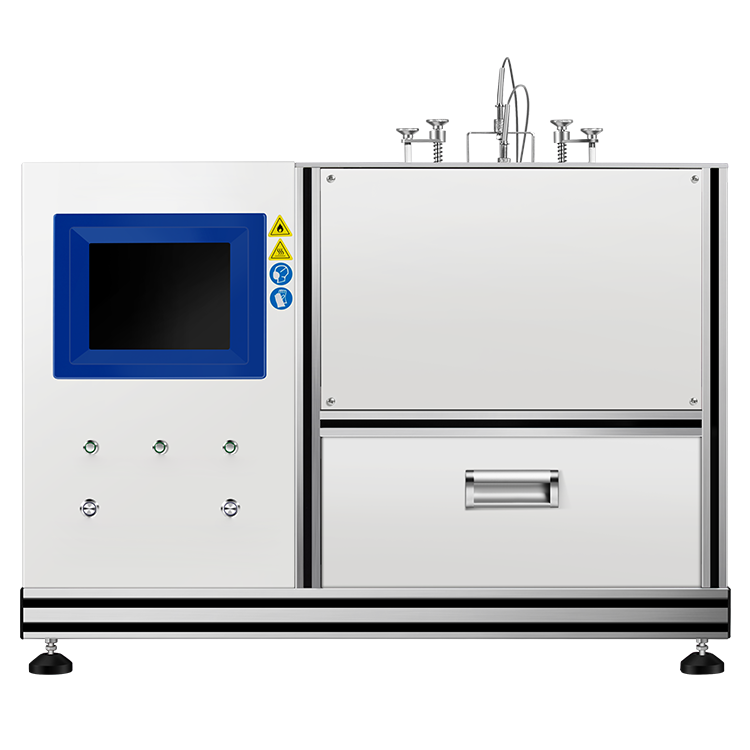
If you are in the field of material science or engineering, you may have heard of a heat flow meter instrument. A heat flow meter is a device that measures the thermal conductivity and thermal resistance of a material. It is commonly used to determine the insulating properties of materials, such as building insulation, packaging materials, and clothing.
The heat flow meter works by measuring the heat transfer through a material. It consists of two plates, one hot and one cold, that sandwich the material being tested. The heat flow meter then measures the temperature difference between the two plates and the rate at which heat is transferred through the material. This information is used to calculate the thermal conductivity and thermal resistance of the material. The heat flow meter is a valuable tool for determining the effectiveness of insulation materials and can help engineers and scientists design more efficient products.
Principles of Heat Flow Measurement
Thermal Conductivity Basics
Thermal conductivity is a measure of a material’s ability to conduct heat. It is defined as the amount of heat that flows through a unit area of a material in a unit time when a temperature gradient is applied. The SI unit of thermal conductivity is watts per meter per Kelvin (W/mK).
Steady-State Heat Transfer
Steady-state heat transfer occurs when the temperature of a system remains constant over time. In this case, the rate of heat transfer is constant and can be measured using a Heat Flow Meter Instrument. The Heat Flow Meter Instrument works by measuring the thermal resistance of a material. The thermal resistance is defined as the ratio of the temperature difference across a material to the rate of heat flow through the material.
Transient Techniques
Transient techniques measure the rate of heat transfer during a change in temperature. This method is useful for measuring the thermal properties of materials that exhibit time-dependent behavior, such as phase-change materials. The Heat Flow Meter Instrument can be used to perform transient measurements by measuring the temperature response of a material to a step change in heat flux.
In summary, the Heat Flow Meter Instrument is a powerful tool for measuring the thermal properties of materials. By using the principles of thermal conductivity, steady-state heat transfer, and transient techniques, the Heat Flow Meter Instrument can provide accurate and reliable measurements of a material’s thermal properties.
Heat Flow Meter Instrument Design
When it comes to measuring thermal conductivity, the heat flow meter instrument is an accurate and easy-to-use device that provides quick results. The instrument’s design consists of several key components that work together to provide accurate readings. In this section, we’ll take a closer look at the design of the heat flow meter instrument, including sensor technology and calibration methods.
Sensor Technology
The heat flow meter instrument uses thin-film heat flux transducers to measure thermal conductivity. These transducers are made up of thin strips of metal that are deposited onto a substrate. When a temperature gradient is applied to the sample being tested, heat flows through the sample and is transferred to the transducers. The transducers then convert the heat into an electrical signal that can be measured and analyzed.
One of the benefits of using thin-film heat flux transducers is that they have a low thermal mass. This means that they respond quickly to changes in temperature, providing accurate readings in real-time. Additionally, the transducers are highly sensitive, allowing for precise measurements of even the smallest changes in thermal conductivity.
Calibration Methods
To ensure accurate readings, heat flow meter instruments must be calibrated regularly. Calibration involves comparing the readings of the instrument to known values, such as those provided by a reference material. There are several methods for calibrating heat flow meter instruments, including:
-
Direct calibration: This method involves using a reference material with a known thermal conductivity value. The instrument is then calibrated against this material, ensuring that its readings are accurate.
-
Indirect calibration: In this method, the instrument is calibrated against a reference material with a known thermal resistance value. The thermal conductivity of the sample being tested is then calculated based on the instrument’s readings and the known thermal resistance of the reference material.
-
Self-calibration: Some heat flow meter instruments are designed to self-calibrate, meaning that they can adjust their readings based on changes in ambient temperature or other factors. This method can be convenient, but it’s important to ensure that the instrument is properly calibrated before use.
In conclusion, the heat flow meter instrument is a valuable tool for measuring thermal conductivity. Its design, including thin-film heat flux transducers and various calibration methods, allows for accurate and precise readings. Whether you’re testing insulation materials or other materials with low thermal conductivity, the heat flow meter instrument is an essential tool for any laboratory or testing facility.
Operational Procedure
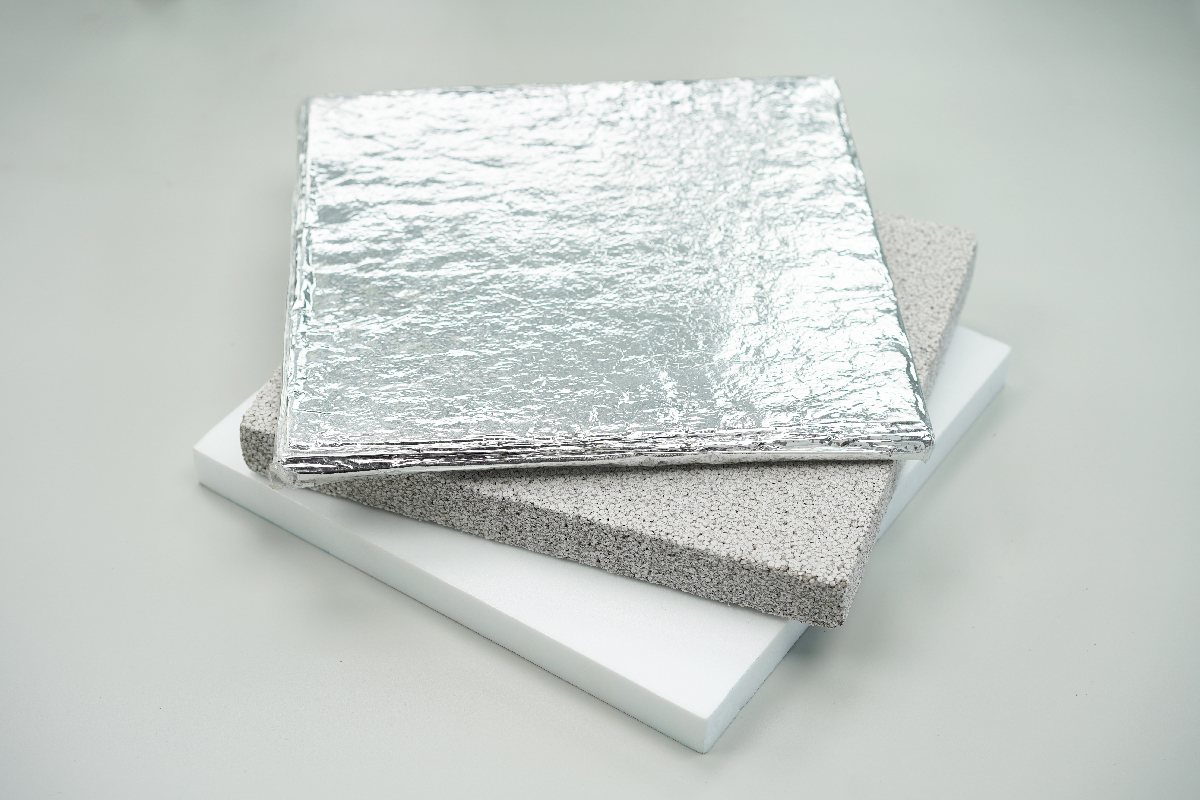
Sample Preparation
Before starting the measurement process, it is important to prepare the sample correctly. The sample should be flat and have a uniform thickness. The thickness of the sample should be measured accurately using a micrometer. The sample should be cut to the appropriate size using a sharp blade or scissors. The edges of the sample should be smooth and free from any defects.
Measurement Process
To start the measurement process, the sample should be placed between the heated and cooled plates of the Heat Flow Meter Instrument. The temperature gradient should be set, and the heat flow meter should be positioned between the sample and the temperature plates. The heat flow meter measures the rate of heat flow through the sample. The temperature gradient and the rate of heat flow through the sample should be recorded.
During the measurement process, it is important to ensure that the sample is in good contact with the temperature plates. Any air gaps between the sample and the plates can lead to errors in the measurement. To minimize the contact resistance, a pneumatic load should be applied to the test stack.
Data Acquisition
Once the measurement process is complete, the data should be recorded and analyzed. The thermal conductivity and thermal transmittance of the sample can be calculated using the data obtained from the measurement process. The data should be analyzed using appropriate software or tools. It is important to ensure that the data is accurate and reliable.
In conclusion, the Heat Flow Meter Instrument is a powerful tool for measuring the thermal conductivity of materials. By following the appropriate operational procedure, accurate and reliable data can be obtained. Proper sample preparation, measurement process, and data acquisition are critical for obtaining accurate results.
Applications of Heat Flow Meters
Heat Flow Meters are widely used in various applications, including building materials, insulation testing, and research and development. In this section, we will discuss the different applications of Heat Flow Meters and how they are used in each application.
Building Materials
Heat Flow Meters are commonly used in the construction industry to measure the thermal conductivity of building materials. This information is critical in determining the energy efficiency of a building. By measuring the thermal conductivity of different building materials, you can determine which materials are best suited for insulation.
Insulation Testing
Heat Flow Meters are also used to test the effectiveness of insulation materials. Insulation is critical in maintaining the energy efficiency of a building. By measuring the thermal conductivity of insulation materials, you can determine which materials are the most effective at preventing heat loss.
Research and Development
Heat Flow Meters are also commonly used in research and development. Researchers use Heat Flow Meters to measure the thermal conductivity of new materials. This information is critical in determining the potential applications of new materials. By measuring the thermal conductivity of new materials, researchers can determine which materials are best suited for specific applications.
Overall, Heat Flow Meters are versatile instruments that are used in various applications. Whether you are in the construction industry, insulation testing, or research and development, Heat Flow Meters are essential tools for measuring thermal conductivity.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Routine Maintenance
To ensure that your Heat Flow Meter Instrument is working optimally, it is important to perform routine maintenance. This includes regular cleaning of the instrument, checking for any signs of wear and tear, and replacing any worn out parts. Additionally, it is important to calibrate the instrument regularly to ensure accurate readings. You can refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for specific maintenance requirements and recommended maintenance schedules.
Common Issues
Despite regular maintenance, there may be some common issues that you may encounter with your Heat Flow Meter Instrument. Some of the most common issues include inaccurate readings, sensor failure, and power supply issues. These issues can be caused by a variety of factors, such as improper installation, environmental factors, or component failure.
Troubleshooting Steps
If you encounter any issues with your Heat Flow Meter Instrument, there are several troubleshooting steps that you can take. First, check the power supply to ensure that the instrument is receiving adequate power. Next, check the sensor connections and wiring to ensure that they are properly connected and not damaged. If you are still experiencing issues, refer to the manufacturer’s troubleshooting guide for more detailed steps.
In addition to these troubleshooting steps, it is important to keep accurate records of any maintenance or repairs performed on the instrument. This can help you identify any recurring issues and determine if any additional maintenance or repairs are necessary. By performing routine maintenance and addressing any issues promptly, you can ensure that your Heat Flow Meter Instrument continues to provide accurate and reliable readings.