Heat Flow Meter Technique: Principles and Applications
The Heat Flow Meter (HFM) is a specialized instrument designed to measure thermal conductivity by assessing heat transfer through a thermal insulation material. It operates by applying heat via a heating element on one side of the material, while the heat transfer is measured on the opposite side. This process allows for the determination of the material’s thermal conductivity coefficient. Accurate measurement of thermal conductivity is essential across various industries, particularly in construction, energy, and electronics. Reliable data aids in optimizing material selection and enhancing performance within these fields.
What is the Heat Flow Meter Technique?
Principle of Operation
The Heat Flow Meter (HFM) technique measures the transfer of heat through materials to determine their thermal conductivity. It uses a heating element to generate heat on one side of the material, while a sensor on the opposite side measures the amount of heat that passes through. By calculating the temperature difference between the two sides, the device determines how well the material conducts heat. The technique operates under steady-state conditions, ensuring precise measurements. This method is widely used in industries such as construction, energy, and electronics for material testing and performance optimization.
Heat Flux Sensors, Temperature Differential, and the Steady-State Method
The HFM uses heat flux sensors to track the flow of heat through a material, detecting the amount of heat transferred at any given moment. These sensors measure the temperature differential between the hot and cold sides of the material, providing crucial data to calculate thermal conductivity. The steady-state method ensures that the system reaches a stable temperature before beginning measurements, offering reliable and consistent results.
Testing Principle
Sample Placement and Temperature Control
For testing, the sample is placed between two plates—one hot and one cold. The system automatically adjusts the temperatures of these plates, ensuring the sample reaches a predefined average temperature. Throughout the test, the temperature difference between the plates remains constant, allowing for accurate heat flow measurement.
Measurement of Heat Flow and Data Collection
Once the system stabilizes at the correct temperature, heat flow through the sample is measured. Data collection begins automatically once thermal equilibrium is reached, and the test concludes once all necessary data is recorded. The heat flow sensor output is calibrated using standard reference materials to ensure the accuracy of the results.
Calculating Thermal Conductivity and Specific Heat Capacity
The software applies Fourier’s law to calculate both thermal conductivity and thermal resistance. It also assesses the relationship between thermal conductivity and plate temperature. Additionally, the device can measure specific heat capacity, making it ideal for testing insulating materials. Testing is fully automated, allowing for fast and precise measurements, while also offering the capability to control the load applied to the sample, which helps analyze the impact of density variation in compressible materials on thermal conductivity.
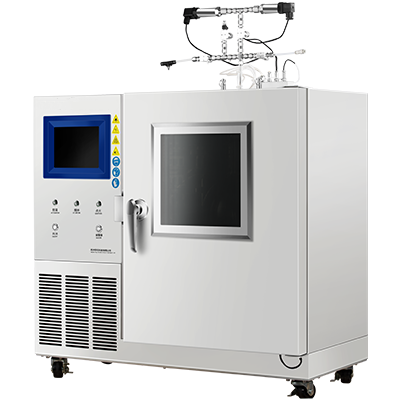
Advantages of the Heat Flow Meter Technique – HFM 510A
Wide Range of Material Testing
The HFM 510A adheres to international standards such as GB/T 10295, ASTM C518, and ISO 8301. And thermal conductivity range is (0.001~2) W/(m·K). It allows for testing a variety of materials with low thermal conductivity, including expanded polystyrene, extruded polystyrene, PU rigid foam, mineral wool, expanded perlite, foam glass, natural fiber materials, cork, wool, aerogel, concrete, and gypsum.
Highly Automated Features
The HFM 510A is equipped with numerous automated functions for ease of use, including automatic lifting and lowering of the heating plate, automatic load force testing, automatic thickness measurement, and automatic temperature control. The device also features automatic furnace door operation, enhancing convenience during testing.
Rapid and Precise Sample Testing
With dual heat flow sensors for increased precision and independent temperature control for the upper and lower plates, the HFM 510A ensures accurate and consistent results. The system’s ability to test materials quickly and reliably is further supported by external oil bath cooling and nitrogen gas purging for sample drying. It also boasts low environmental sensitivity and a wide temperature range, ensuring stability during testing.
Versatile and Flexible Operation
The HFM 510A is adaptable to irregular sample surfaces and includes molds for particle sample preparation, making the process more efficient. The device’s software supports extended thermal conductivity accessory modes and can operate offline, providing flexibility in various experimental settings. It also allows fully automated data collection, real-time monitoring, and automatic generation of test reports. Optional user login features enable access to historical records, and the device supports customizable data storage and export.
The HFM 510A is designed with expandability in mind, featuring a built-in industrial computer and easy peripheral connectivity (e.g., mouse, keyboard, printer). The high-definition touchscreen display and intuitive human-machine interface enhance user experience, combining functionality with elegant design.
Applications of Heat Flow Meter Technique
Building Insulation Materials
The Heat Flow Meter technique plays a critical role in testing building insulation materials, determining their effectiveness in insulating against heat. Accurate thermal conductivity measurements are essential for selecting the most energy-efficient materials for construction.
Thermal Insulation Materials
The technique is widely employed in testing thermal insulation materials used across industries like construction, refrigeration, and energy. The HFM ensures that these materials meet the required performance standards for optimal thermal insulation.
Refrigeration Materials
In the refrigeration industry, where thermal properties are crucial, the Heat Flow Meter technique helps assess the materials used in refrigeration systems. It ensures that the materials provide the appropriate thermal conductivity, contributing to better system performance and energy efficiency.
In Closing
The HFM 510A is a highly precise and efficient device designed for measuring thermal conductivity. It operates by placing a sample between two plates—one hot and one cold—while automatically adjusting the temperatures to maintain a steady heat flow. The device enables fast, accurate testing, leveraging its automated features. It measures thermal conductivity, thermal resistance, and specific heat capacity, making it ideal for testing both insulating materials and compressible materials with varying densities. Compliant with international standards, the HFM 510A ensures reliable results. Its user-friendly interface and fully automated data collection streamline the testing process, making it both simple and efficient.