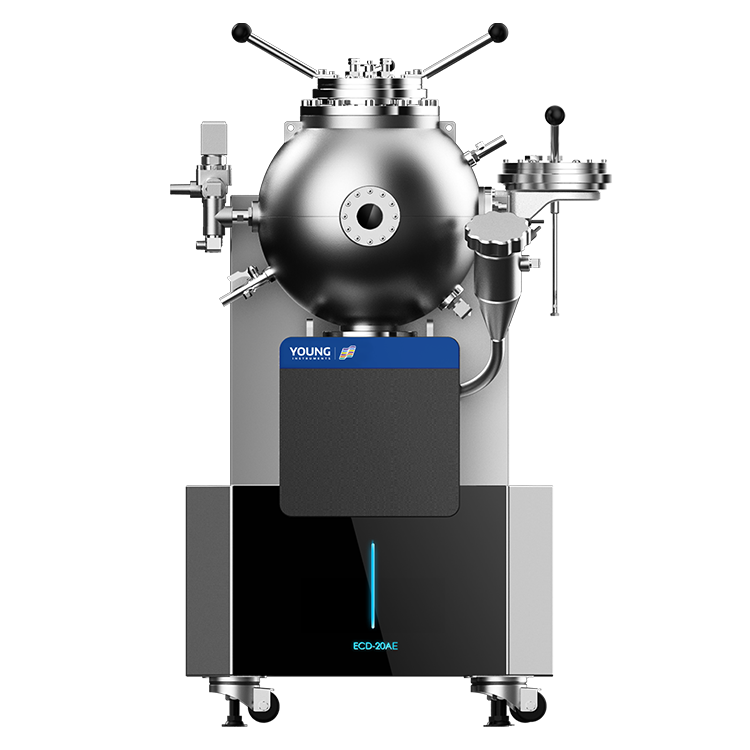
Ignition Sensitivity Testing: Understanding the Basics
If you work with materials that are used in oxygen or other reactive environments, ignition sensitivity testing is a critical step in ensuring safety. Ignition sensitivity testing is the process of determining how easily a material can be ignited by various stimuli, such as impact, friction, or electrostatic discharge. This information is used to determine whether the material is safe to handle and use in its intended environment, as well as to identify potential hazards and develop appropriate safety measures.
There are various methods for conducting ignition sensitivity testing, including ASTM G86, which describes test equipment and techniques for determining the impact sensitivity of materials in oxygen under different conditions. Other tests may be performed to evaluate the friction sensitivity or electrostatic discharge sensitivity of a material. These tests are typically performed on all materials that will be used in oxygen or other reactive environments to ensure that they are safe to handle and use.
Fundamentals of Ignition Sensitivity
Definitions and Key Concepts
Ignition sensitivity refers to the susceptibility of a material to ignite or initiate a reaction upon exposure to an external stimulus. This stimulus can be in the form of heat, flame, impact, friction, or other sources of energy. The extent of the reaction can vary from a mild reaction to a violent explosion, depending on the material’s properties and the conditions of the stimulus.
The ignition sensitivity of a material can be influenced by various factors such as its chemical composition, physical properties, environmental conditions, and the type and intensity of the stimulus. It is important to understand the ignition sensitivity of a material to ensure safe handling, storage, and transportation, especially in industries that deal with hazardous materials such as explosives, pyrotechnics, and aerospace.
Importance of Measuring Ignition Sensitivity
Measuring the ignition sensitivity of a material is crucial to assess its safety and performance characteristics. It helps to identify the potential hazards associated with the material and to develop appropriate safety measures to mitigate the risks. It also provides valuable information for the design and optimization of processes and equipment that involve the use of the material.
Ignition sensitivity testing is typically performed under controlled laboratory conditions using specialized equipment and procedures. The test methods involve exposing the material to various types and intensities of stimuli and observing its reaction. The results are then analyzed to determine the material’s sensitivity threshold and to compare it with the established safety standards and regulations.
In summary, understanding the fundamentals of ignition sensitivity is essential for ensuring safety and performance in industries that deal with hazardous materials. Measuring the ignition sensitivity of a material is a critical step in assessing its safety and optimizing its use.
Test Methodologies
Standard Test Procedures
Ignition sensitivity testing is a critical safety test used to evaluate the relative sensitivity of materials to ignition by various gaseous fluid media. The test is performed using standard test procedures such as ASTM E2019 and G-74. These tests evaluate the sensitivity of materials to dynamic pressure impacts by various gaseous fluid media, which may include mixtures of gases. The results of these tests provide a relative measure of ignition sensitivity of a material or batch-to-batch acceptance data.
Sample Preparation
Sample preparation is a crucial aspect of ignition sensitivity testing. Any change or variations in test specimen configurations, thickness, preparation, and cleanliness may cause a significant change in impact sensitivity. It is essential to prepare the samples according to the test method’s specifications to ensure accurate and consistent results. The samples should be free from any contamination and should be prepared to the correct thickness and dimensions.
Environmental Controls
Environmental controls are necessary during ignition sensitivity testing. Temperature, humidity, and pressure can all affect the test results. The testing environment should be controlled to ensure accurate and consistent results. The test should be performed in a controlled environment to eliminate any variables that may affect the test results. The test chamber should be designed to meet the test method’s specifications and should be equipped with the necessary environmental controls.
In conclusion, ignition sensitivity testing is a critical safety test used to evaluate the relative sensitivity of materials to ignition by various gaseous fluid media. The test is performed using standard test procedures such as ASTM E2019 and G-74. Sample preparation and environmental controls are crucial aspects of ignition sensitivity testing and should be performed according to the test method’s specifications to ensure accurate and consistent results.
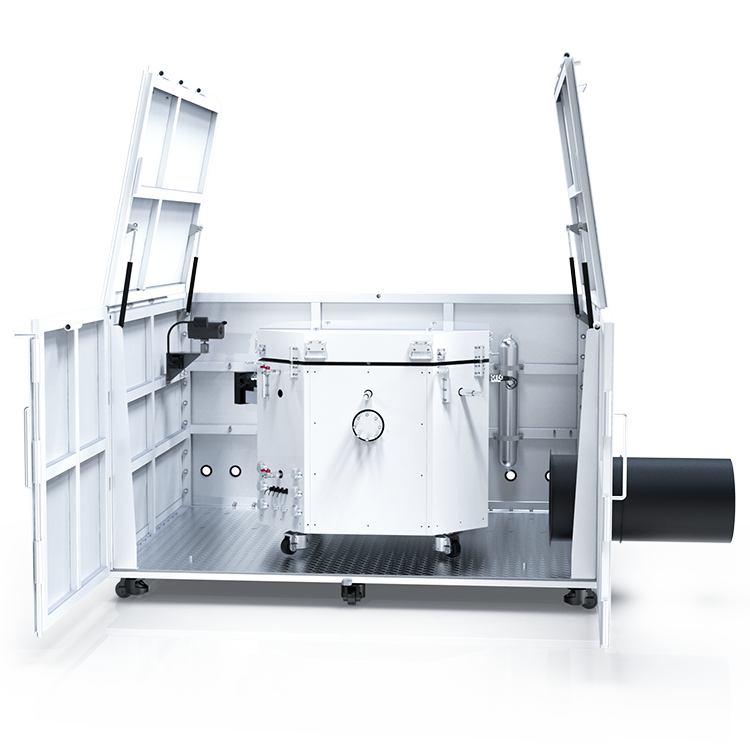
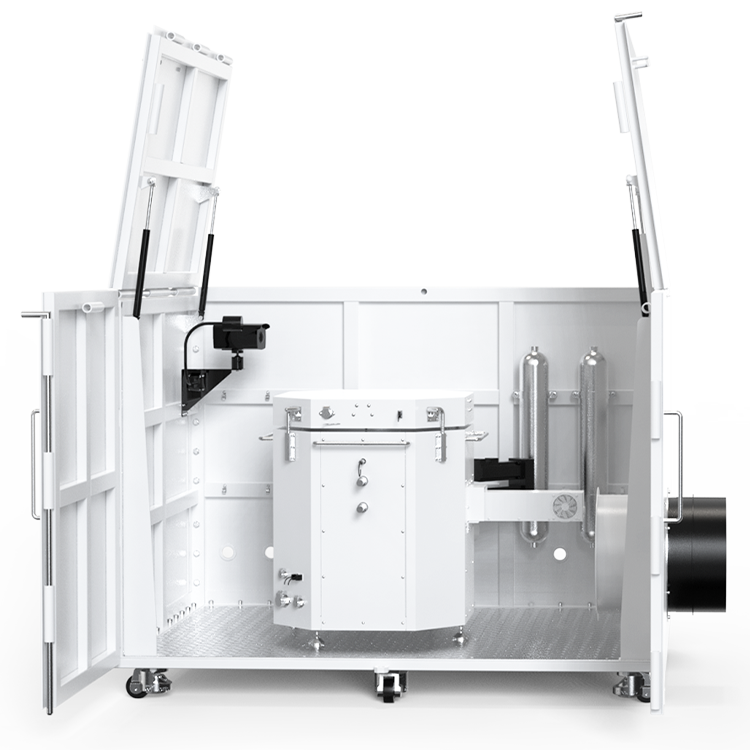
Instrumentation and Equipment
When performing ignition sensitivity testing, it is important to use appropriate instrumentation and equipment to ensure accurate and safe results. This section will cover the two main categories of equipment needed for this testing: ignition sensitivity measurement devices and safety precautions and equipment.
Ignition Sensitivity Measurement Devices
There are several types of ignition sensitivity measurement devices available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common types of devices used for this testing include:
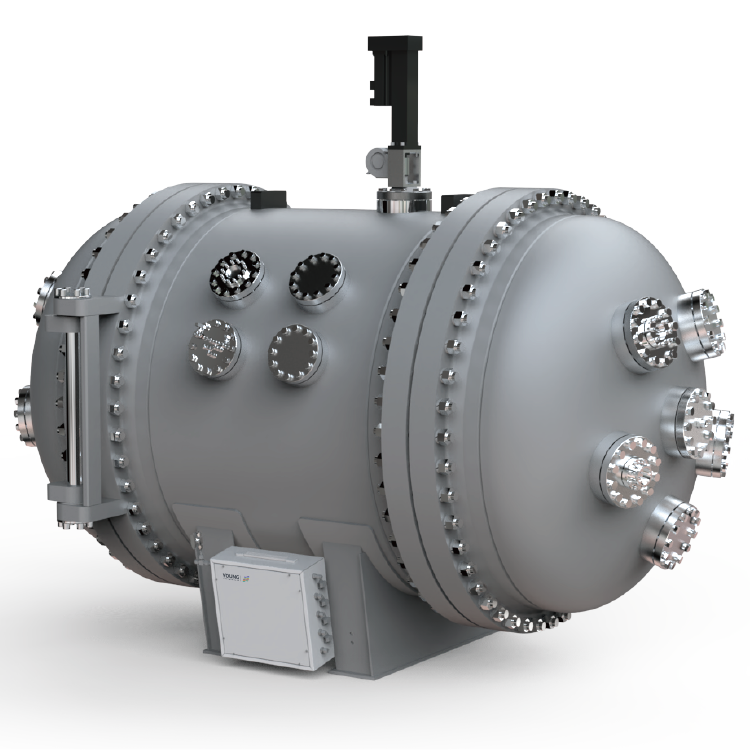
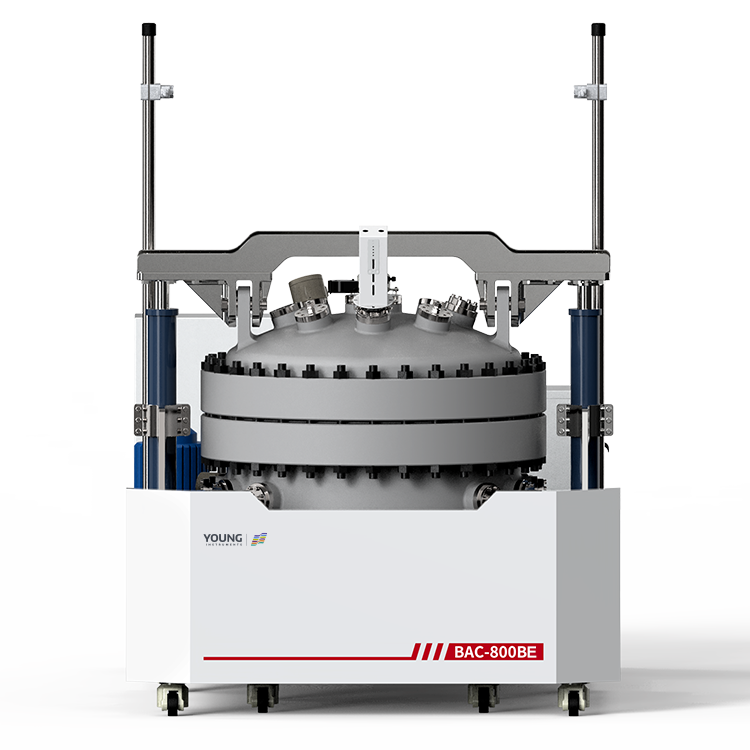
- Gaseous Fluid Impact Sensitivity (GFIS) Test Systems: These systems utilize a high-pressure source to directly attach materials and components, and have minimal volume between the material/component and the pressure source. ASTM G74-13(2021) describes two GFIS test systems, a 5 mm GFIS system and a 14 mm GFIS system.
- Drop Weight Impact Testers: These testers use a weight that is dropped onto a sample to determine its sensitivity. ASTM E2546-16 describes a procedure for this type of testing.
- Friction Sensitivity Testers: These testers measure the sensitivity of a material to friction. ASTM D2021-17 outlines a procedure for this type of testing.
Safety Precautions and Equipment
When performing ignition sensitivity testing, safety must be a top priority. The following equipment and precautions should be taken to ensure a safe testing environment:
- Safety Glasses: These should be worn at all times during testing to protect your eyes from any flying debris or particles.
- Gloves: Wear gloves to protect your hands from any sharp or hazardous materials.
- Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation in the testing area to prevent any buildup of hazardous gases or fumes.
- Fire Extinguisher: Have a fire extinguisher readily available in case of any unexpected fires.
- Remote Valve Sequencer: This controls the opening and closing of the test chamber pressurization (impact) and vent valves during the test so that each impact/ vent cycle will be completed in identical, prescribed time periods.
By using appropriate instrumentation and safety equipment, you can ensure accurate and safe ignition sensitivity testing.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
Data Processing
After conducting the Ignition Sensitivity Testing, you will need to process the data obtained from the test. The first step is to organize the data in a table or spreadsheet. In the table, you should include the sample name, the ignition delay time, and the corresponding pressure and temperature values. It is essential to ensure that the data is accurate and complete.
Once you have organized the data, you should check for any outliers or errors. Any data that appears to be abnormal or inconsistent should be removed from the dataset. This will ensure that the analysis is based on reliable data.
Statistical Analysis
After processing the data, you can proceed to conduct statistical analysis. The most common statistical analysis method used in Ignition Sensitivity Testing is the linear regression analysis. This method involves plotting the ignition delay time against the pressure and temperature values. The slope of the regression line represents the ignition sensitivity of the sample.
It is essential to note that the statistical analysis should be conducted using appropriate software such as Microsoft Excel or MATLAB. These software packages have built-in functions that can help you conduct the analysis accurately and efficiently.
In conclusion, data analysis and interpretation are critical in Ignition Sensitivity Testing. It is essential to ensure that the data is accurate and complete before conducting any statistical analysis. The statistical analysis should be conducted using appropriate software, and the results should be interpreted with caution.
Applications and Implications
Material Classification
Ignition sensitivity testing plays a critical role in the classification of materials. The sensitivity of a material to ignition is often used to determine its level of danger. This classification is important in determining how the material should be handled, transported, and stored. Ignition sensitivity testing can help to identify materials that are prone to ignition and can help to prevent accidents and incidents.
Risk Assessment
Ignition sensitivity testing is an important tool in risk assessment. By measuring the sensitivity of a material to ignition, it is possible to identify potential hazards and assess the risk associated with handling, storing, and transporting the material. This information can be used to develop appropriate safety protocols and procedures to minimize the risk of accidents.
Regulatory Compliance
Ignition sensitivity testing is often required by regulatory bodies to ensure compliance with safety regulations. For example, the US Department of Transportation requires that materials that are prone to ignition be properly labeled and transported in accordance with specific regulations. Ignition sensitivity testing can help to ensure that materials are properly classified and labeled, and can help to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Overall, ignition sensitivity testing is a critical tool in the safe handling, storage, and transportation of materials. By identifying materials that are prone to ignition, it is possible to develop appropriate safety protocols and procedures to minimize the risk of accidents and incidents. Ignition sensitivity testing is also important for compliance with regulatory requirements and for risk assessment.