Limiting Oxygen Concentration Test: Understanding the Basics
If you work in an industry that deals with flammable materials, then you may have heard of the Limiting Oxygen Concentration (LOC) test. This test is used to determine the minimum concentration of oxygen in a mixture of fuel, air, and inert gas that is required for combustion to occur. The LOC test is essential for preventing fires and explosions in industries such as mining, chemical manufacturing, and oil and gas production.
The LOC test is used to determine the concentration of oxygen required for combustion to occur, but it also helps to identify the upper and lower flammability limits (UFL and LFL) of a substance. The UFL and LFL are the maximum and minimum concentrations of a substance in air that will support combustion. Knowing the UFL and LFL of a substance is essential for preventing fires and explosions because it allows you to control the concentration of the substance in the air to prevent combustion.
The LOC test is an important tool for preventing fires and explosions in industries that deal with flammable materials. It helps to determine the minimum concentration of oxygen required for combustion to occur and identifies the upper and lower flammability limits of a substance. By understanding the UFL and LFL of a substance, you can control the concentration of the substance in the air to prevent combustion and ensure the safety of your workers and facilities.
Fundamentals of Limiting Oxygen Concentration
Definition and Importance
The Limiting Oxygen Concentration (LOC) is the minimum concentration of oxygen required to sustain combustion in a given mixture of fuel and oxidizer. The LOC test is a critical safety measure used in industrial settings to prevent fires and explosions.
Knowing the LOC of a particular mixture is essential for designing safe processes and handling of flammable materials. It helps determine the minimum amount of inert gas required to prevent combustion, and is used to establish safe operating procedures in hazardous environments.
Theoretical Background
The LOC test is based on the principle of oxygen dilution. As the concentration of oxygen in a mixture decreases, the likelihood of combustion decreases as well. The LOC is determined by gradually decreasing the oxygen concentration in a mixture until combustion can no longer be sustained.
There are several methods for determining the LOC, including ASTM E2079 and EN 14034-4. These methods involve measuring the concentration of oxygen in the mixture and gradually reducing it until combustion is no longer sustained. The LOC value is then calculated based on the concentration of oxygen at which combustion ceased.
In summary, the LOC test is a critical safety measure used in industrial settings to prevent fires and explosions. It is based on the principle of oxygen dilution and involves gradually reducing the concentration of oxygen in a mixture until combustion can no longer be sustained. Knowing the LOC of a particular mixture is essential for designing safe processes and handling flammable materials.
Test Methodologies
Standard Test Procedures
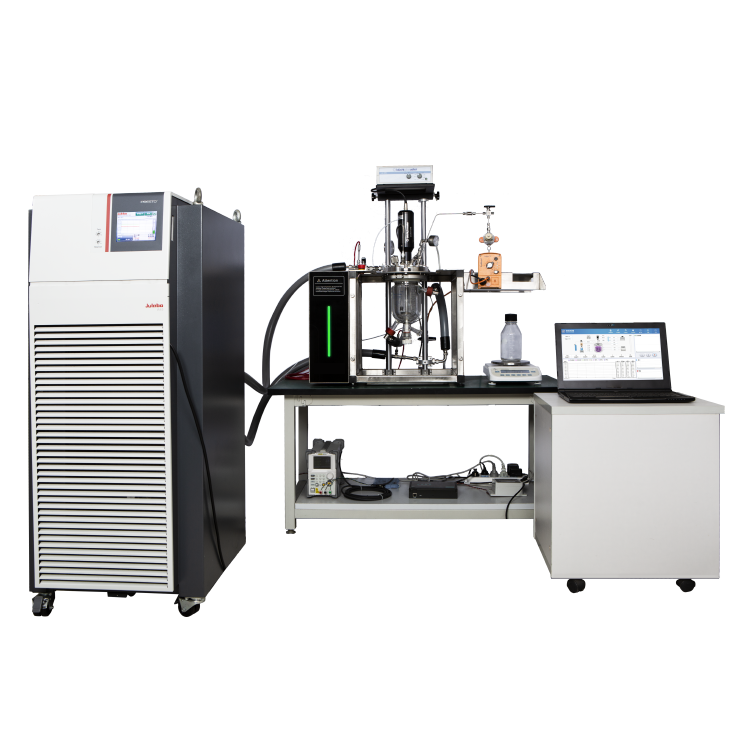
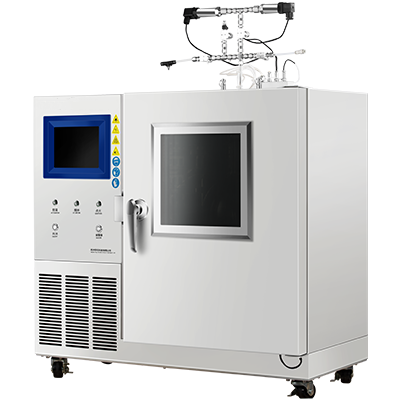
The Limiting Oxygen Concentration (LOC) test is used to determine the minimum concentration of oxygen required to support combustion in a mixture of oxygen, inert gases, and flammable gases or vapors. The test is conducted per ASTM E2079-19, which specifies the test procedures and apparatus to be used.
The standard test method involves introducing a mixture of oxygen, inert gas, and flammable gas or vapor into a sealed chamber. The initial pressure and temperature of the mixture are specified in the test standard. The oxygen concentration is gradually reduced until combustion is no longer sustained. The minimum oxygen concentration required to sustain combustion is the LOC value.
Sample Preparation
Before conducting the LOC test, the sample mixture should be prepared according to the test standard. The flammable gas or vapor should be mixed with the inert gas and oxygen to the desired concentration. The sample mixture should be thoroughly mixed and allowed to stabilize at the specified temperature and pressure before conducting the test.
Safety Precautions
The LOC test involves the use of flammable gases and vapors, which can pose a fire or explosion hazard. Therefore, it is important to take appropriate safety precautions when conducting the test.
Some safety precautions that should be taken include:
- Conducting the test in a well-ventilated area or fume hood
- Using appropriate personal protective equipment, such as safety glasses, gloves, and a lab coat
- Keeping sources of ignition, such as flames or sparks, away from the test area
- Following the manufacturer’s instructions for the equipment used in the test
- Having a fire extinguisher or other means of extinguishing a fire readily available
By following the standard test procedures and taking appropriate safety precautions, you can accurately determine the limiting oxygen concentration of a mixture of oxygen, inert gases, and flammable gases or vapors.
Analysis and Interpretation
Data Collection
During the Limiting Oxygen Concentration (LOC) test, the oxygen concentration is gradually reduced in the test vessel until ignition occurs. The data collected during the test includes the oxygen concentration at ignition and the pressure and temperature inside the test vessel. This data is used to calculate the LOC value, which is the minimum oxygen concentration in a gas mixture that will support combustion.
To ensure accurate data collection, it is important to follow the test procedure carefully and use calibrated equipment. The oxygen concentration should be measured using a calibrated oxygen analyzer with a sensitivity of 0.1 mol% oxygen, such as a paramagnetic analyzer or gas chromatography. The test vessel should be of a suitable size for the gas mixture being tested, and the temperature and pressure should be monitored throughout the test.