The Impact of Charging Rates on Heat and Gas Generation Induced by Thermal Runaway in Lithium Batteries under High-Temperature and Overcharge Conditions
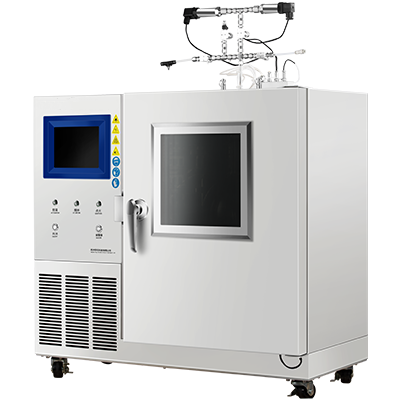
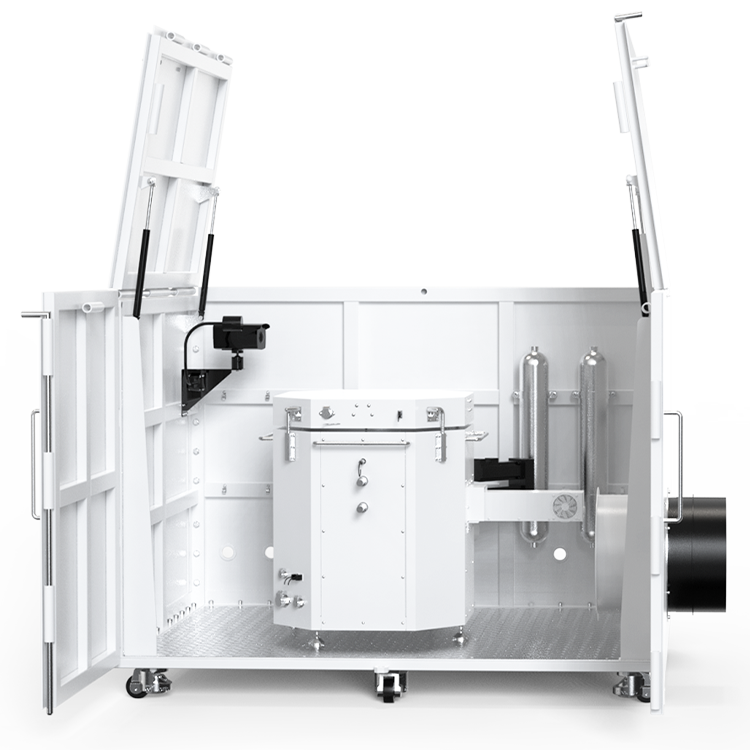
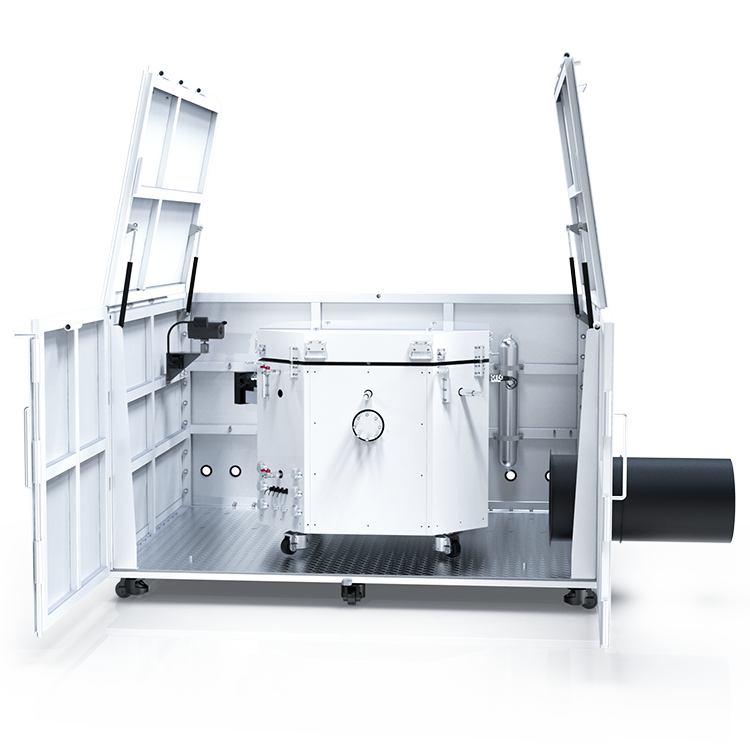
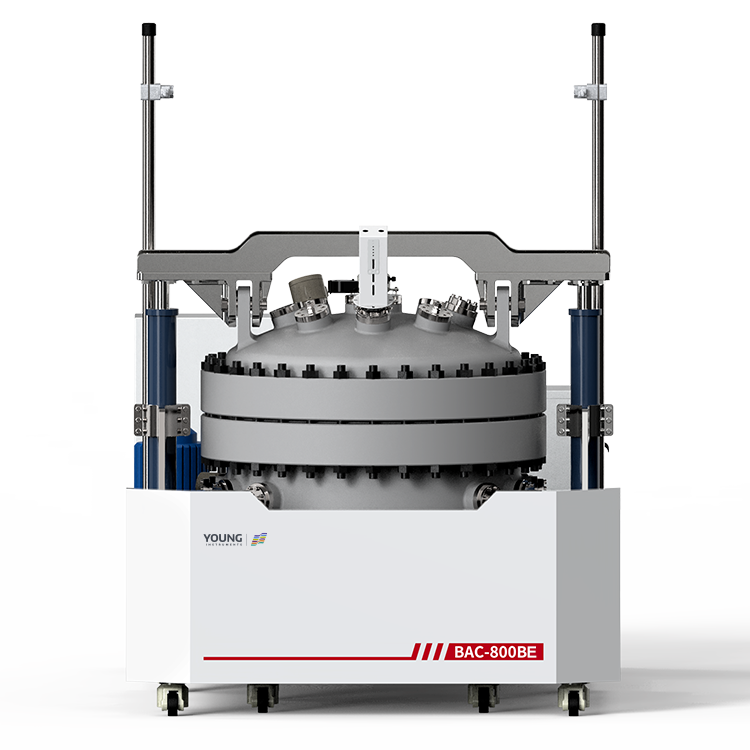
Professor Han Dong’s research group from Shanghai Jiao Tong University, including Dr. Guo Qian Zhen, published a paper titled “Effects of charging rates on heat and gas generation in lithium-ion battery thermal runaway triggered by high temperature coupled with overcharge” in the Journal of Power Sources. This study utilized the Small Battery Adiabatic Calorimeter(BAC-90AE) as the primary testing instrument to investigate the impact of different charging rates on the heat and gas generation in lithium-ion batteries during thermal runaway events triggered by high temperatures and overcharging conditions.
Application of BAC-90AE in this study:
The experiment employed the Small Battery Adiabatic Calorimeter(BAC-90AE) in conjunction with a battery testing system to study the thermal runaway behavior of 18650-type NCM batteries under high-temperature conditions. The findings indicate:
- Under the combined effects of high temperature and charging behavior, batteries are more susceptible to thermal runaway. An increase in charging rate leads to the production of more irreversible heat and intensifies side reactions, thus promoting the occurrence of thermal runaway and enhancing the battery’s capacity for heat and gas generation.

- The influence of charging behavior on thermal runaway exhibits a nonlinear relationship, primarily due to the combined effects of the charging phase and charging current on the promotion of side reactions.

- During the thermal runaway process, the relationship between the gas generation rate and the heat generation rate can be divided into two linear growth stages. In the initial stage, the gas generation rate is consistent across different charging rates, but in the subsequent stage, as the charging rate increases, the gas generation rate shows differences, indicating a change in the side reaction pathways.

The research findings are of significant importance for understanding the mechanism of thermal runaway triggered by charging under high-temperature environments and provide a reference for the safety and performance optimization of lithium-ion batteries in various applications.