Thermal Hazards Tester: What You Need to Know
If you work with chemicals, you know that safety is a top priority. When working with reactive chemicals, it’s important to be aware of potential thermal hazards. Thermal hazards occur when a chemical reaction generates more heat than can be dissipated, leading to an increase in temperature and pressure. This can result in a fire or explosion.

To prevent thermal hazards, it’s important to conduct thermal stability testing. This involves collecting reaction rate data and applying that data to assess whether a specified quantity of material can be used in a way such that runaway reactions are avoided. A comprehensive lab uses many tools to understand and eliminate undesired reactions. One of these tools is a thermal hazards tester, which measures the heat generated during a chemical reaction. By measuring the heat generated, scientists can determine whether the reaction is exothermic (releasing heat) or endothermic (absorbing heat). This information is crucial in understanding the potential for thermal hazards.
Fundamentals of Thermal Hazards Testing
Thermal hazards testing is a critical process that helps ensure the safety of products and processes that involve heat. This testing involves evaluating the potential for thermal hazards, such as fire or explosion, that may result from the use of a product or process. The testing is typically performed by subjecting the product or process to various temperatures and pressures to determine its susceptibility to thermal hazards.
One of the key components of thermal hazards testing is the use of calorimetry. Calorimetry is the measurement of the heat released or absorbed by a system during a chemical reaction or physical change. This measurement is critical for determining the potential for thermal hazards, as it provides information about the amount of heat that may be produced by a reaction or process.
During thermal hazards testing, a variety of factors are evaluated, including the thermal stability of the product or process, the potential for thermal runaway reactions, and the ignition temperature of the product or process. This information is used to develop safety protocols and guidelines for the use of the product or process, as well as to identify potential hazards and develop strategies for mitigating them.
Some common types of thermal hazards testing include adiabatic calorimetry, differential scanning calorimetry, and thermal stability testing. Each of these tests provides valuable information about the potential for thermal hazards associated with a product or process and can be used to develop effective safety protocols.
Overall, thermal hazards testing is a critical process for ensuring the safety of products and processes that involve heat. By evaluating the potential for thermal hazards and developing effective safety protocols, this testing helps to minimize the risk of fire or explosion and ensure the safety of workers and consumers alike.
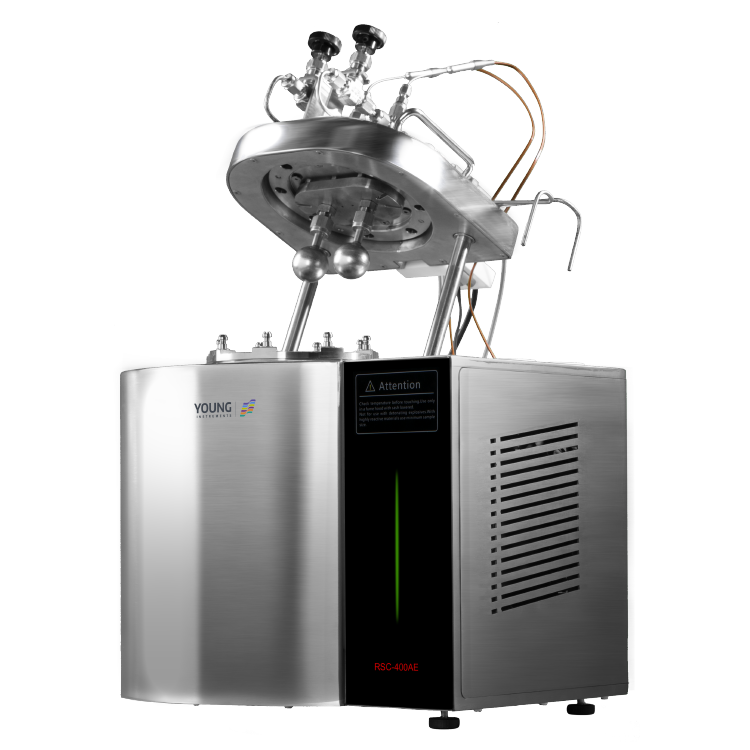
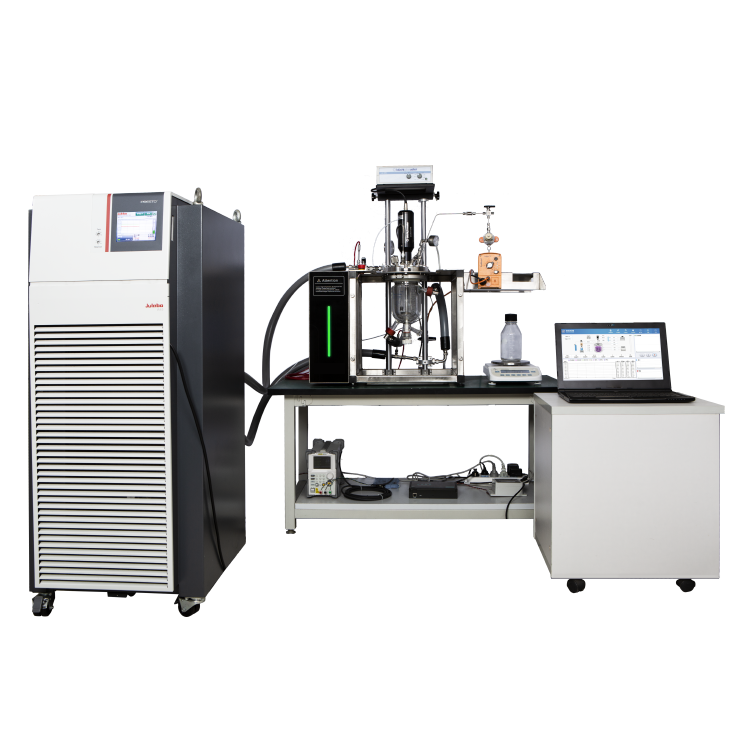
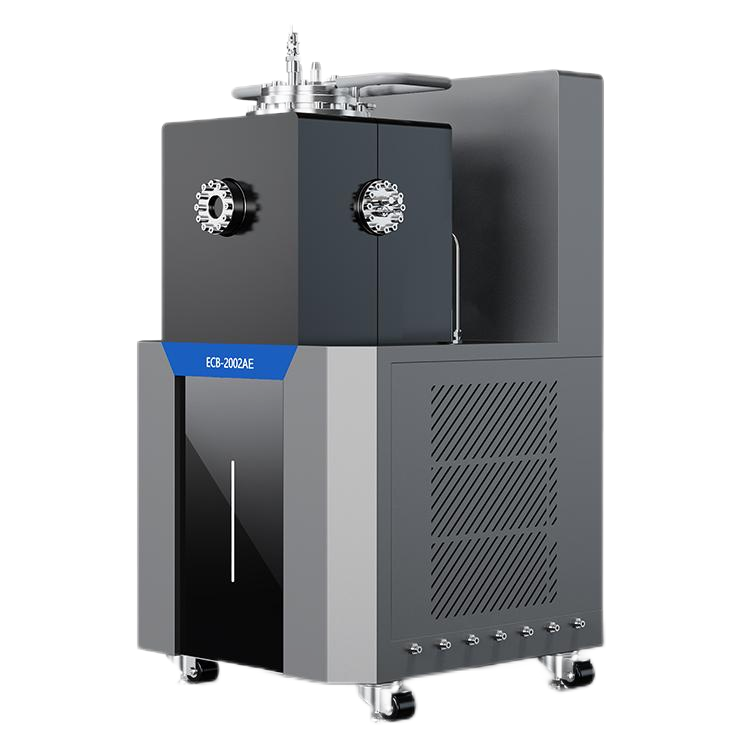
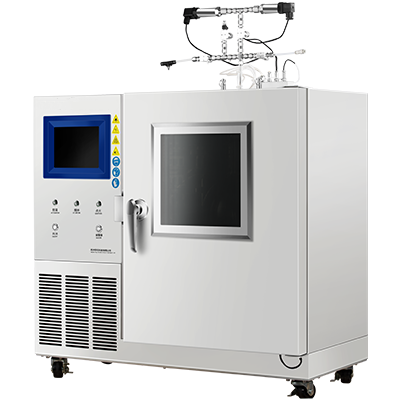
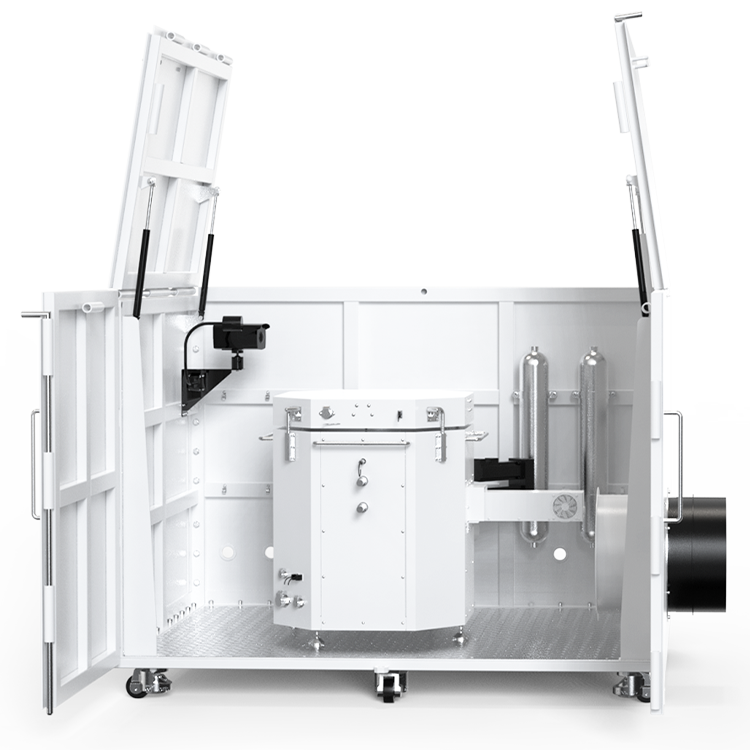
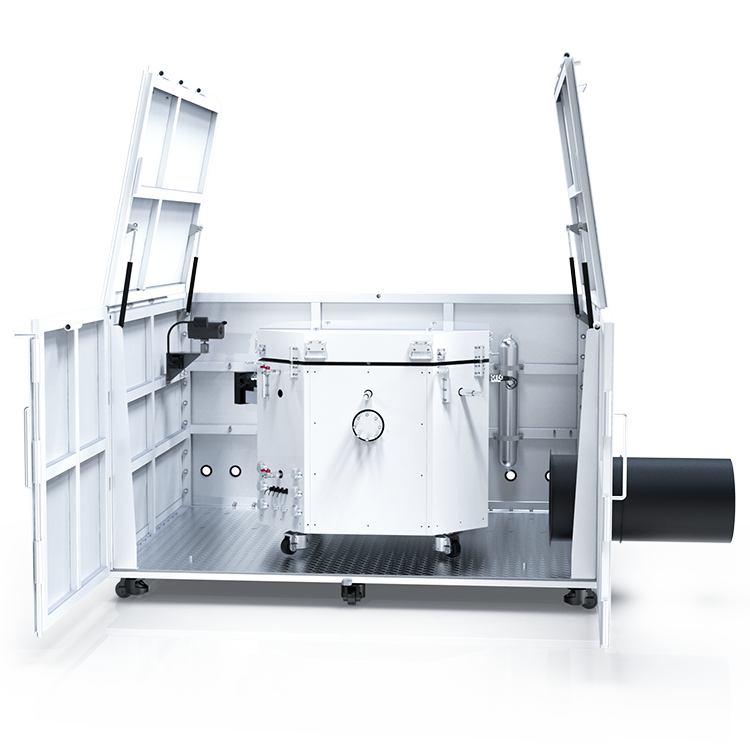
Thermal Hazards Tester Design
When it comes to designing a Thermal Hazards Tester, there are several important factors to consider. In this section, we will discuss the instrumentation, safety features, and user interface of a typical Thermal Hazards Tester.
Instrumentation
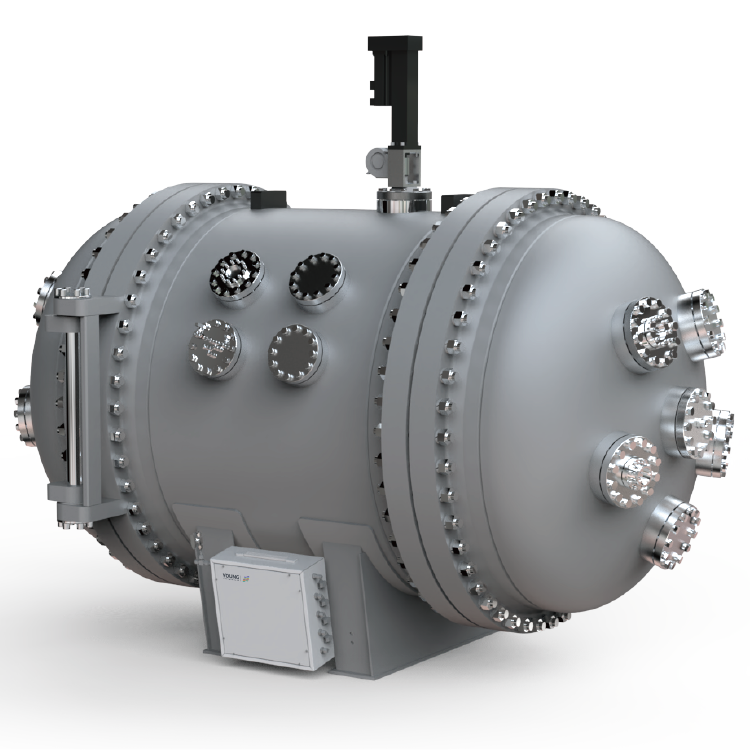
The instrumentation of a Thermal Hazards Tester is critical to accurately measuring the thermal properties of a material. A typical Thermal Hazards Tester will include a calorimeter, which measures the heat generated by a sample as it undergoes a thermal reaction. The calorimeter is typically surrounded by a water jacket, which helps to control the temperature of the sample and prevent it from overheating.
In addition to the calorimeter, a Thermal Hazards Tester may also include a thermocouple, which measures the temperature of the sample. This information is used to calculate the heat of reaction and other important thermal properties.
Safety Features
Safety is a top priority when designing a Thermal Hazards Tester. To ensure the safety of the user and the surrounding environment, a Thermal Hazards Tester may include several safety features. For example, the instrument may be equipped with a pressure relief valve, which releases excess pressure in the event of a runaway reaction. The instrument may also include a cooling system, which helps to prevent the sample from overheating.
Other safety features may include a fire extinguisher, emergency stop button, and an alarm system to alert the user in the event of a problem.
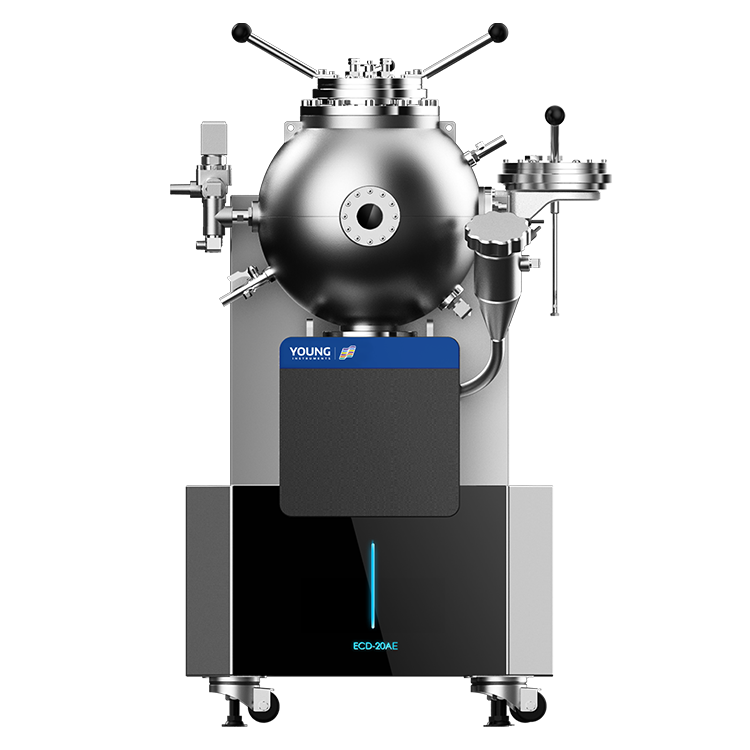
User Interface
The user interface of a Thermal Hazards Tester is designed to be user-friendly and intuitive. The interface typically includes a touchscreen display, which allows the user to control the instrument and view real-time data. The user may also be able to program the instrument to run specific tests or protocols.
In addition to the touchscreen display, the user interface may include a variety of buttons and switches for controlling the instrument. The user interface may also include a data logging system, which allows the user to store and analyze data from previous experiments.
Overall, the design of a Thermal Hazards Tester is critical to accurately and safely measure the thermal properties of a material. By incorporating high-quality instrumentation, robust safety features, and a user-friendly interface, a Thermal Hazards Tester can provide valuable insights into the thermal behavior of a material.
Testing Procedures
When it comes to testing for thermal hazards, there are several procedures that need to be followed to ensure accurate and reliable results. These procedures include sample preparation, test execution, and data analysis.
Sample Preparation
Before conducting any tests, it is important to properly prepare the samples. This involves selecting the appropriate sample size and shape, as well as ensuring that the sample is free of any contaminants that could affect the results. It is also important to properly label the samples to avoid any confusion during testing.
Test Execution
Once the samples have been prepared, it is time to conduct the tests. This involves exposing the samples to various temperatures and monitoring their behavior. The exact testing parameters will depend on the specific thermal hazards being tested for, as well as the standards and regulations that apply to your industry.
During testing, it is important to closely monitor the samples and record any observations. This includes measuring the temperature of the samples, as well as any changes in their physical properties or behavior.
Data Analysis
After the testing is complete, it is time to analyze the data. This involves reviewing the observations and measurements taken during the test, as well as comparing the results to any applicable standards or regulations.
During data analysis, it is important to look for any trends or patterns in the results. This can help identify any potential hazards or areas for improvement. It is also important to properly document the results and any conclusions drawn from the data analysis.
Overall, following these testing procedures is essential for ensuring accurate and reliable results when testing for thermal hazards. Proper sample preparation, test execution, and data analysis are all critical components of any effective testing program.
Applications of Thermal Hazards Testing
Thermal hazards testing is a crucial step in evaluating reactive chemical hazards. It is a process of identifying the potential hazards and risks associated with a substance, process, or system by analyzing its thermal behavior. This testing can be applied in various industries such as chemical, pharmaceuticals, material science, and more. In this section, we will discuss the applications of thermal hazards testing in different industries.
Chemical Industry
In the chemical industry, thermal hazards testing is a critical component of process safety management. It helps to identify the potential hazards associated with chemical reactions and processes, such as runaway reactions, thermal decomposition, and thermal stability. The data obtained from thermal hazards testing can be used to design safe processes, select appropriate equipment, and develop emergency response plans.
Pharmaceuticals
Pharmaceutical companies use thermal hazards testing to evaluate the thermal stability of their products. It helps to identify the risks associated with the storage, handling, and transportation of drugs. Thermal hazards testing can also be used to determine the shelf life of a drug and to develop appropriate packaging and storage conditions.
Material Science
Thermal hazards testing is also used in material science to evaluate the thermal stability and flammability of materials. It helps to identify the potential hazards associated with materials and to develop appropriate safety measures. The data obtained from thermal hazards testing can be used to design safe products, select appropriate materials, and develop appropriate handling and storage procedures.
In conclusion, thermal hazards testing is an essential tool in identifying potential hazards and risks associated with substances, processes, and systems. It is widely used in various industries such as chemical, pharmaceuticals, material science, and more. By using thermal hazards testing, you can ensure the safety of your products, processes, and personnel.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Routine Maintenance
Regular maintenance of your Thermal Hazards Tester is essential to ensure its optimal performance. Here are some routine maintenance tips:
- Always keep the device clean and dry. Use a soft cloth to wipe the surface of the device.
- Check the cables and connectors for any damages or wear and tear. Replace them immediately if you find any issues.
- Inspect the heating element for any damages or discoloration. Replace it if necessary.
- Keep the device calibrated to ensure accurate readings. Follow the calibration instructions in the user manual.
Error Handling
Despite regular maintenance, you may encounter some errors while using your Thermal Hazards Tester. Here are some common errors and their solutions:
- Error Code 1: This error indicates a problem with the heating element. Check the heating element for any damages or discoloration. Replace it if necessary.
- Error Code 2: This error indicates a problem with the temperature sensor. Check the sensor for any damages or wear and tear. Replace it if necessary.
- Error Code 3: This error indicates a problem with the power supply. Check the power supply and cables for any damages or wear and tear. Replace them if necessary.
If you encounter any other errors, consult the user manual or contact technical support for assistance.
Technical Support
If you encounter any issues with your Thermal Hazards Tester, contact our technical support team for assistance. Our team of experts is available to help you with any technical issues you may encounter. You can reach our technical support team via email or phone. Please have your device serial number and error code ready when you contact us.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
When it comes to thermal hazards testing, regulatory standards and compliance are crucial. Compliance with industry standards ensures that your product is safe and meets all necessary requirements.
One important standard to consider is UL 94, which evaluates the flammability of plastic materials. UL 94 classifies materials based on their burning characteristics, with the highest classification being V-0, indicating that the material is highly resistant to ignition and will self-extinguish within 10 seconds.
Another important standard is IEC 60695, which outlines test methods for determining the flammability of materials used in electronic and electrical equipment. This standard includes several different tests, including the glow wire test and the needle flame test.
Compliance with these standards is essential for ensuring that your product is safe and meets all necessary requirements. Failure to comply with these standards can result in serious consequences, including fines, product recalls, and damage to your brand’s reputation.
To ensure compliance, it is important to work with a reputable testing laboratory that is accredited to perform the necessary tests. These laboratories have the expertise and equipment necessary to perform accurate and reliable testing, and can provide you with the documentation you need to demonstrate compliance with regulatory standards.