Vapor Pressure Tester: What It Is and How It Works
If you work with fuels, chemicals, or other substances that require precise measurements of vapor pressure, then a vapor pressure tester is an essential tool for your lab. A vapor pressure tester measures the pressure exerted by the vapor of a substance in a sealed container at a given temperature. This measurement is important for understanding the volatility and stability of a substance, which can affect its performance and safety.
Vapor pressure testers come in a range of sizes and capabilities, from small handheld units to large, automated systems that can test multiple samples at once. They use a variety of methods to measure vapor pressure, including the Reid method, which involves heating a sample and measuring the pressure of the resulting vapor, and the static method, which measures the pressure of the vapor in a sealed container at a fixed temperature. Some vapor pressure testers can also measure other properties of a substance, such as density, viscosity, and flash point.
Fundamentals of Vapor Pressure
Definition and Concepts
A vapor pressure tester is a device that measures the pressure exerted by the vapor of a liquid when it is in equilibrium with its own liquid phase. Vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by the vapor of a liquid at a given temperature in a closed container. The vapor pressure of a liquid increases with temperature. At a certain temperature, known as the boiling point, the vapor pressure equals the atmospheric pressure and the liquid boils.
The vapor pressure of a liquid is affected by several factors, including the intermolecular forces between the molecules of the liquid, the temperature, and the molecular weight of the liquid. Liquids with weak intermolecular forces tend to have higher vapor pressures than those with strong intermolecular forces.
Measurement Principles
The measurement of vapor pressure is based on the principle of partial pressures. The vapor pressure tester measures the partial pressure of the vapor in a closed container. The total pressure inside the container is the sum of the partial pressure of the vapor and the pressure of the gas above the liquid.
There are several methods for measuring vapor pressure, including the Reid vapor pressure method, which is widely used in the petroleum industry, and the static method, which is used for measuring the vapor pressure of non-volatile liquids. In the Reid vapor pressure method, a sample of the liquid is placed in a container and heated to a specific temperature. The pressure of the vapor is then measured, and the vapor pressure is calculated.
In summary, a vapor pressure tester is a device that measures the pressure exerted by the vapor of a liquid when it is in equilibrium with its own liquid phase. The vapor pressure of a liquid is affected by several factors, including the intermolecular forces between the molecules of the liquid, the temperature, and the molecular weight of the liquid. The measurement of vapor pressure is based on the principle of partial pressures, and there are several methods for measuring vapor pressure, including the Reid vapor pressure method and the static method.
Vapor Pressure Tester Design
When it comes to vapor pressure testers, there are two main components that make up the design: the components and assembly and the sensor technology. Understanding these two aspects can help you select the right vapor pressure tester for your needs.
Components and Assembly
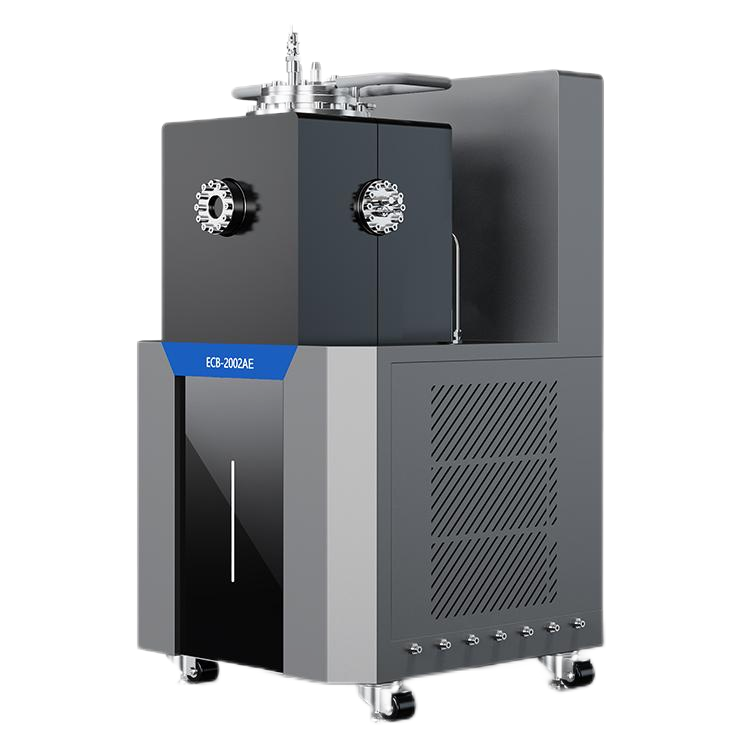
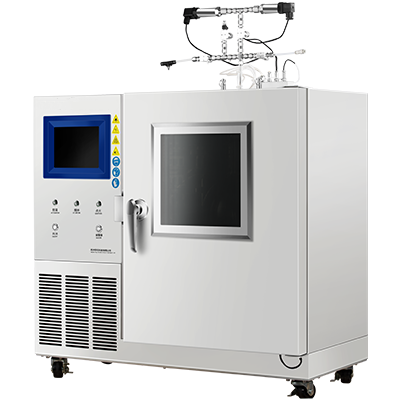
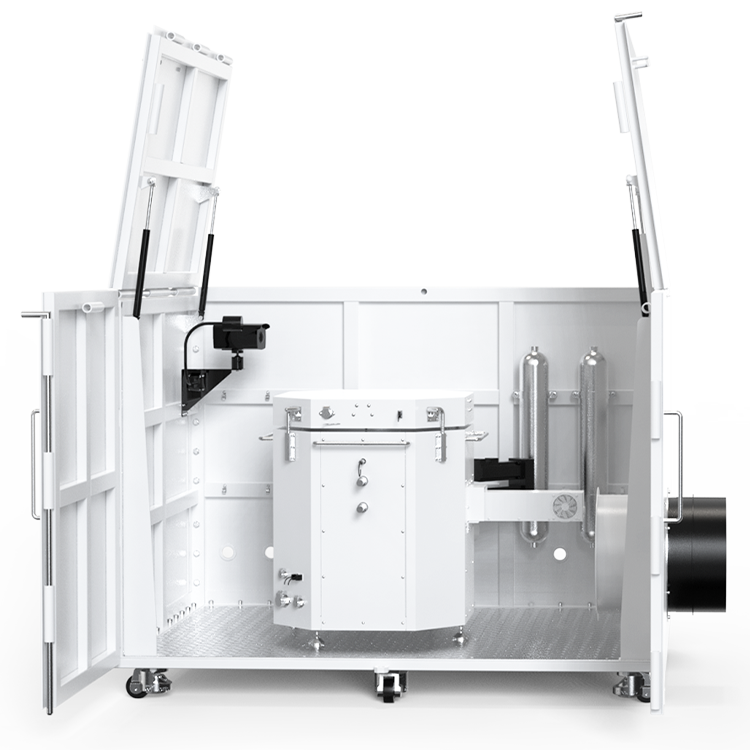
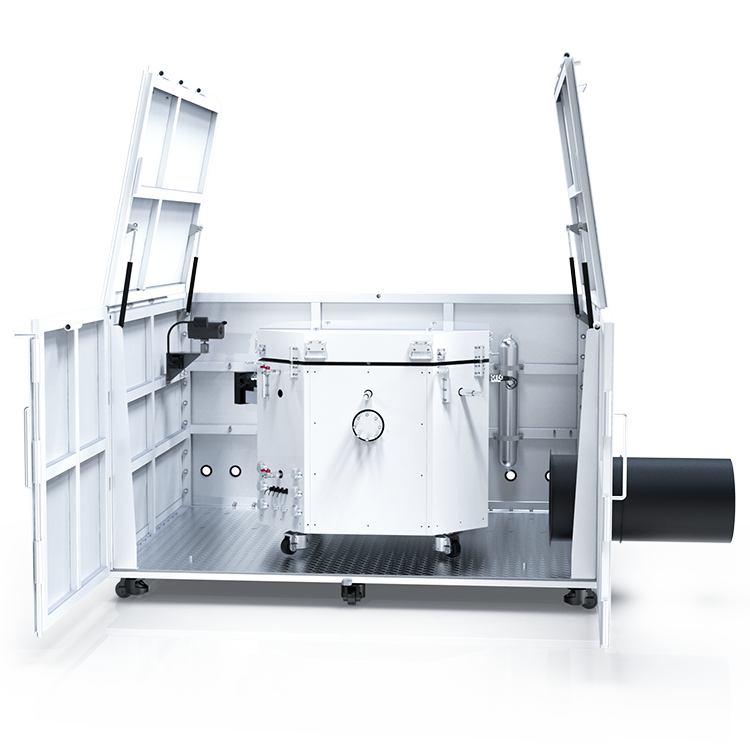
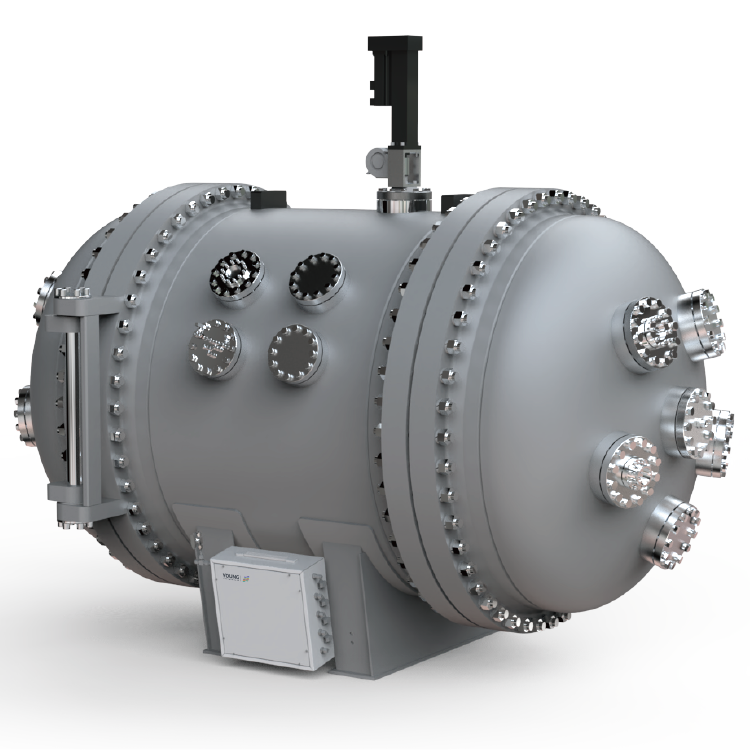
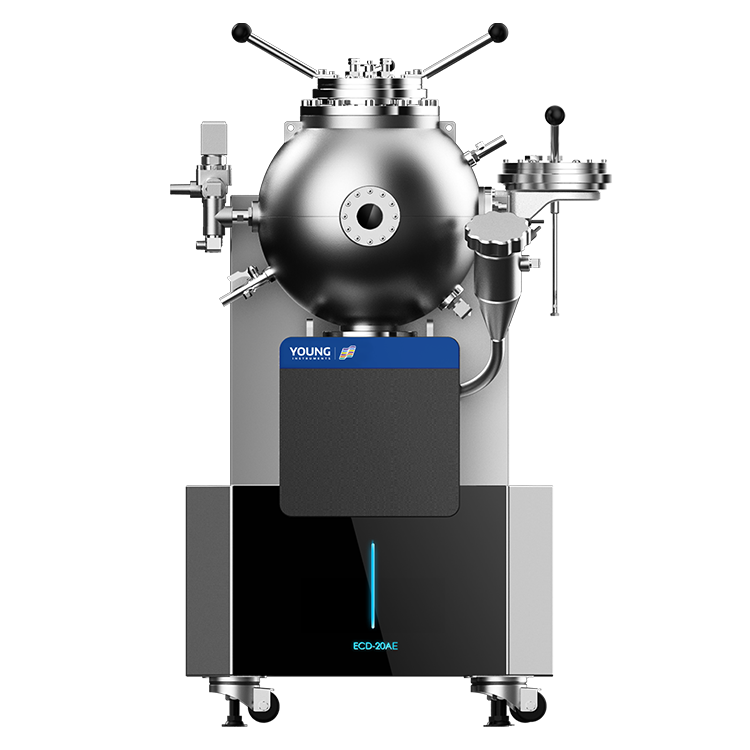
The components and assembly of a vapor pressure tester can vary depending on the manufacturer and model. However, most vapor pressure testers consist of a sample chamber, pressure sensor, temperature sensor, and display/control unit.
The sample chamber is where the sample is placed for testing. It is typically made of stainless steel and has a sealed lid to prevent any leaks during testing. The pressure sensor measures the pressure of the vapor in the sample chamber, while the temperature sensor measures the temperature of the sample.
The display/control unit is where you can view the results of the test and control the settings of the tester. It is typically a digital display with buttons for adjusting settings.
Sensor Technology
The sensor technology used in vapor pressure testers can also vary depending on the manufacturer and model. However, most vapor pressure testers use either a piezoresistive or capacitive pressure sensor.
Piezoresistive pressure sensors use a piezoresistive material that changes resistance when subjected to pressure. Capacitive pressure sensors use a diaphragm that moves in response to pressure, changing the capacitance of the sensor.
Both types of sensors are highly accurate and reliable, but capacitive sensors are typically more sensitive and have a faster response time.
Overall, understanding the components and assembly and sensor technology of vapor pressure testers can help you select the right one for your needs. It is important to consider factors such as pressure range, temperature range, accuracy, and reliability when selecting a tester.
Operation of Vapor Pressure Testers
Vapor pressure testers are used to determine the vapor pressure of volatile liquids and petroleum products. The test is performed by heating the sample in a closed container and measuring the pressure of the vapor that is produced. This information can be used to determine the volatility and evaporation rate of the sample.
Test Procedures
The test procedures for vapor pressure testers may vary depending on the specific instrument being used. However, most testers follow similar steps. First, the sample is placed in a sealed container. The container is then placed in a temperature-controlled bath and heated to a specific temperature. As the temperature increases, the vapor pressure of the sample increases, and the pressure inside the container is measured.
Different methods can be used to measure the pressure of the sample. For example, the Reid Vapor Pressure (RVP) test method measures the pressure inside the container using a pressure gauge. Other methods may use electronic sensors or other types of equipment.
Safety Protocols
When operating a vapor pressure tester, it is essential to follow proper safety protocols to prevent accidents and ensure accurate results. Here are some safety protocols to keep in mind:
- Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as gloves and safety glasses, when handling samples and operating the instrument.
- Follow all manufacturer instructions for the specific instrument being used.
- Do not exceed the recommended temperature or pressure limits for the instrument.
- Use only approved solvents and samples in the instrument.
- Ensure that the instrument is properly grounded to prevent electrical shocks.
- Keep the instrument and surrounding area clean and free of debris.
- Always use caution when handling hot samples and equipment.
By following proper test procedures and safety protocols, you can ensure accurate and safe operation of your vapor pressure tester.
Applications of Vapor Pressure Testers
Vapor pressure testers are used in a variety of industries and research and development settings to measure the vapor pressure of liquids. The information gathered by these devices can be used to determine the quality and stability of a liquid, as well as its boiling point and other important characteristics.
Industrial Use
In the industrial sector, vapor pressure testers are commonly used to measure the vapor pressure of fuels, including gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel. This information is important for ensuring that the fuel meets industry standards and is safe for use in engines and other machinery. Vapor pressure testers are also used in the chemical industry to measure the vapor pressure of solvents and other chemicals. This information is useful for determining the safety and stability of these chemicals, as well as their suitability for use in various applications.
Research and Development
In research and development settings, vapor pressure testers are used to measure the vapor pressure of new materials and compounds. This information is important for determining the properties of these materials, including their boiling point, volatility, and stability. Vapor pressure testers are also used in the pharmaceutical industry to measure the vapor pressure of drugs and other compounds. This information is useful for determining the safety and efficacy of these drugs, as well as their suitability for use in various applications.
In addition to the above applications, vapor pressure testers are also used in a variety of other industries and settings, including the food and beverage industry, the oil and gas industry, and the environmental testing industry. Whether you are a researcher, a chemist, an engineer, or a quality control specialist, a vapor pressure tester can be an invaluable tool for ensuring the quality and safety of your products and materials.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Routine Maintenance
To ensure accurate and reliable vapor pressure measurements, it is important to perform routine maintenance on your vapor pressure tester. Regular maintenance will help to extend the life of your equipment and prevent costly repairs.
Here are some routine maintenance tasks that you should perform on your vapor pressure tester:
- Clean the instrument after each use to prevent contamination.
- Check the calibration of the temperature measurement of the pressure transducer.
- Check the calibration values of the temperature.
- Adjust and control the pressure transducer.
Common Issues and Solutions
Even with routine maintenance, issues may arise with your vapor pressure tester. Here are some common issues and solutions:
- Instrument not turning on: Check to make sure the power cord is plugged in securely and the outlet is functioning properly. If the issue persists, contact technical support.
- Incorrect readings: If you notice that your vapor pressure tester is giving incorrect readings, check the calibration of the temperature measurement of the pressure transducer. If the calibration is correct, check for any leaks or damage to the equipment. If the issue persists, contact technical support.
- Leaking cell: If you notice that your cell is leaking, it may be due to worn O-ring/valve packing. Replace the piston O-ring and try to tighten the valve first. If unsuccessful, replace the valve.
By performing routine maintenance and addressing common issues, you can ensure that your vapor pressure tester is functioning properly and providing accurate and reliable measurements.